Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 181-185
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i4.181
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i4.181
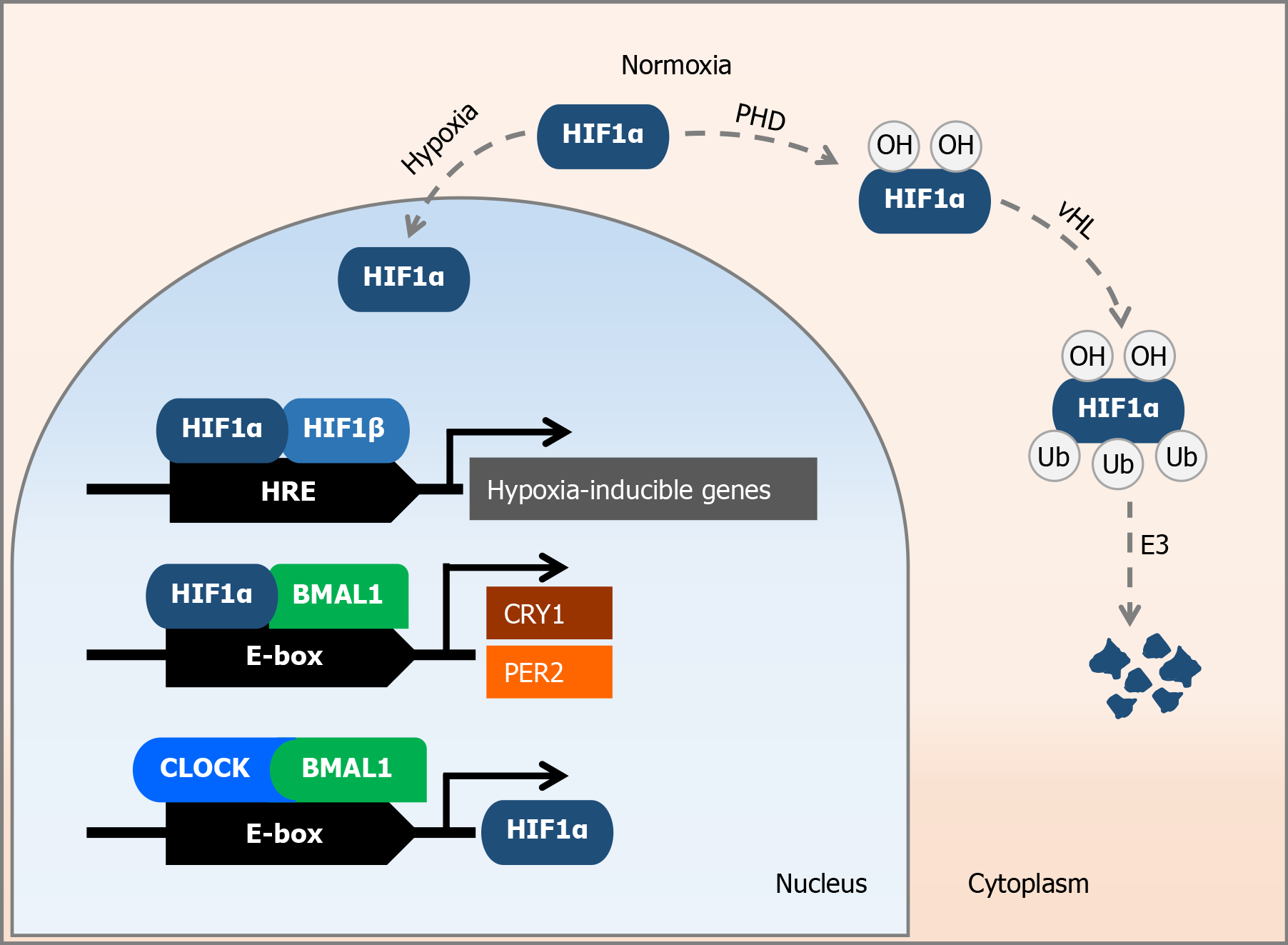
Figure 1 Molecular effects of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α under normal oxygen conditions and under oxygen deprivation.
Under normal oxygen conditions, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system via an oxygen-dependent pathway involving prolyl hydroxylases, the von Hippel-Lindau protein, and an E3 ubiquitin ligase. In the case of an oxygen shortage – hypoxia, HIF1α in the cell nucleus dimerizes with HIF1β, and binds itself to hypoxia response elements, which are associated with hypoxia-inducible genes. Furthermore, the HIF1α-basic helix-loop-helix ARNT like 1 (BMAL1) heterodimer binds to the specific E-box region of circadian genes, thereby enhancing the expression of period circadian regulator 2 and cryptochrome circadian regulator 1. In addition, the BMAL1-circadian locomotor output cycles kaput heterodimer enhances HIF1α expression under hypoxic conditions. HIF1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; PHD: Prolyl hydroxylases; vHL: von Hippel-Lindau protein; HRE: Hypoxia response elements; BMAL1: Basic helix-loop-helix ARNT like 1; PER2: Period circadian regulator 2; CRY1: Cryptochrome circadian regulator 1; CLOCK: Circadian locomotor output cycles kaput.
- Citation: Škrlec I, Kolomeichuk SN. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in myocardial infarction. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(4): 181-185
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i4/181.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i4.181