Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2023; 15(6): 293-308
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i6.293
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i6.293
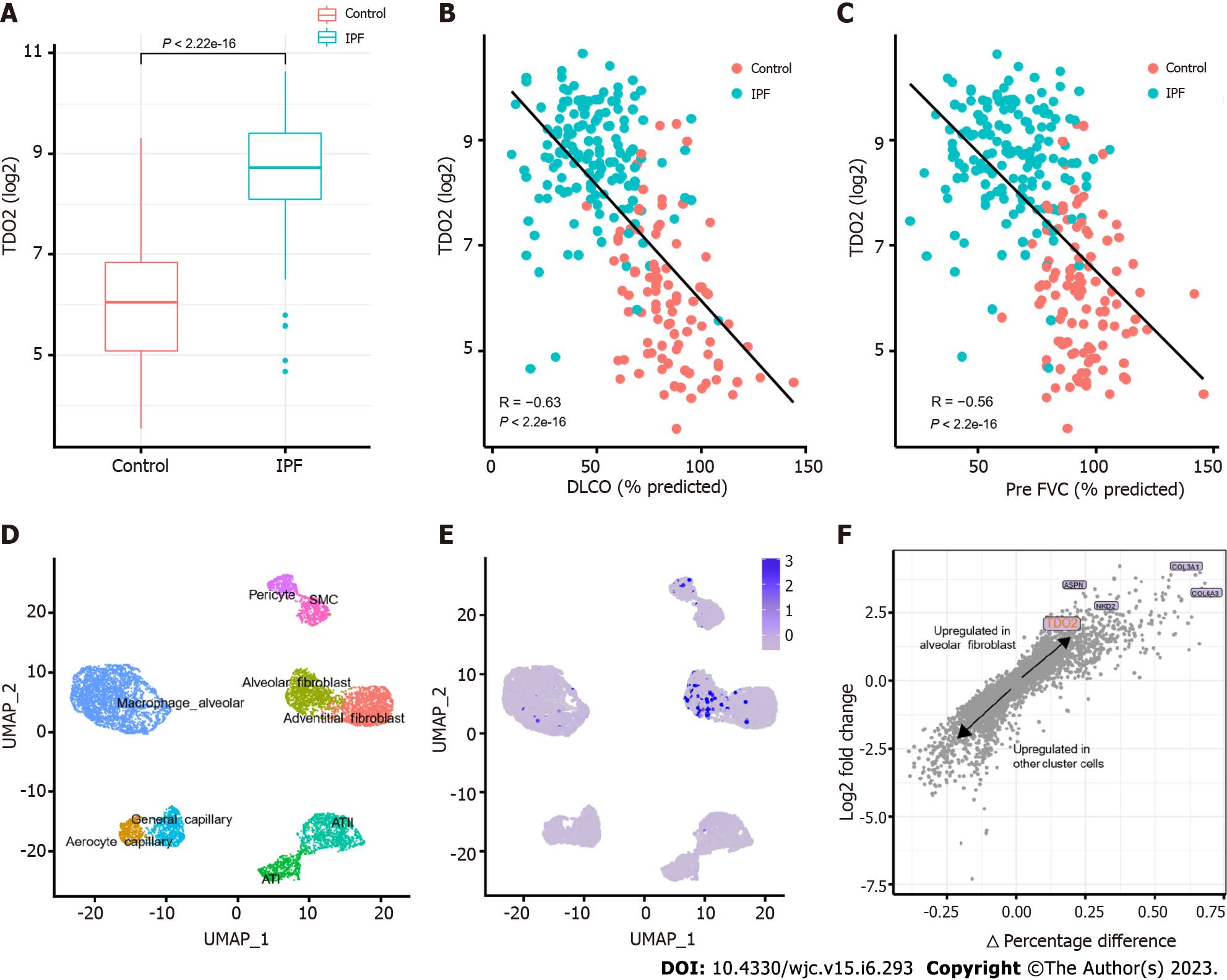
Figure 7 TDO2 increased in Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and was validated in scRNA-seq data.
A: Upregulation of TDO2 in Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis of trained data (e.g., in GSE47460). The statistical test used was the t test; B and C: Correlations between lung TDO2 expression and diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide (B) and forced vital capacity (C) in GSE47460. The Pearson correlation metric was computed by using the ‘stat_cor’ function in R; D: UMAP of 8,942 randomly selected resident lung parenchymal cells from GSE136831; E: UMAP with cells labelled by normalized TDO2 expression; F: Differential gene expression analysis using the log-fold change expression vs the difference in the percentage of cells expressing the gene comparing alveolar fibroblast cluster vs other cluster cells (Δ Percentage Difference). Labelled genes have a log2-fold change > 1, Δ Percentage Difference > 20% and adjusted P value from Wilcoxon rank sum test < 0.05. DLCO: Diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide; IPF: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; FVC: Forced vital capacity.
- Citation: Wang R, Yang YM. Identification of potential biomarkers for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and validation of TDO2 as a potential therapeutic target. World J Cardiol 2023; 15(6): 293-308
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v15/i6/293.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v15.i6.293