Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Cardiol. May 26, 2022; 14(5): 307-318
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i5.307
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i5.307
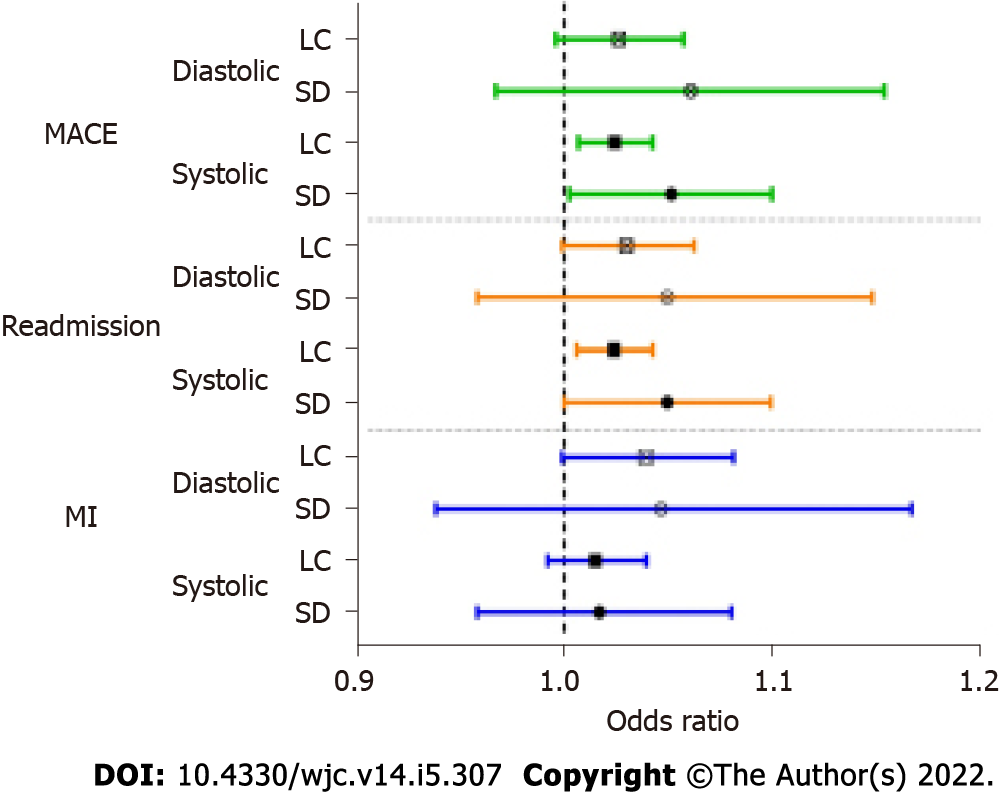
Figure 1 Adjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals from logistic regressions of preoperative blood pressure variability predicting outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention.
Odds ratios were controlled for age, sex, smoking status, diagnoses of hypertension or diabetes, prior cardiovascular disease, prior myocardial infarction, prior coronary artery bypass graft, prior percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), prior creatinine, anginal class, on anti-anginal medications, indication, and average systolic or diastolic blood pressure. Due to some missing values, myocardial infarction was not adjusted for PCI LVEF and creatinine. MACE: Major adverse cardiac events; MI: Myocardial infarction; LC: Largest change; SD: Standard deviation.
- Citation: Weisel CL, Dyke CM, Klug MG, Haldis TA, Basson MD. Day-to-day blood pressure variability predicts poor outcomes following percutaneous coronary intervention: A retrospective study. World J Cardiol 2022; 14(5): 307-318
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v14/i5/307.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v14.i5.307