Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Cardiol. Mar 26, 2022; 14(3): 108-138
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.108
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.108
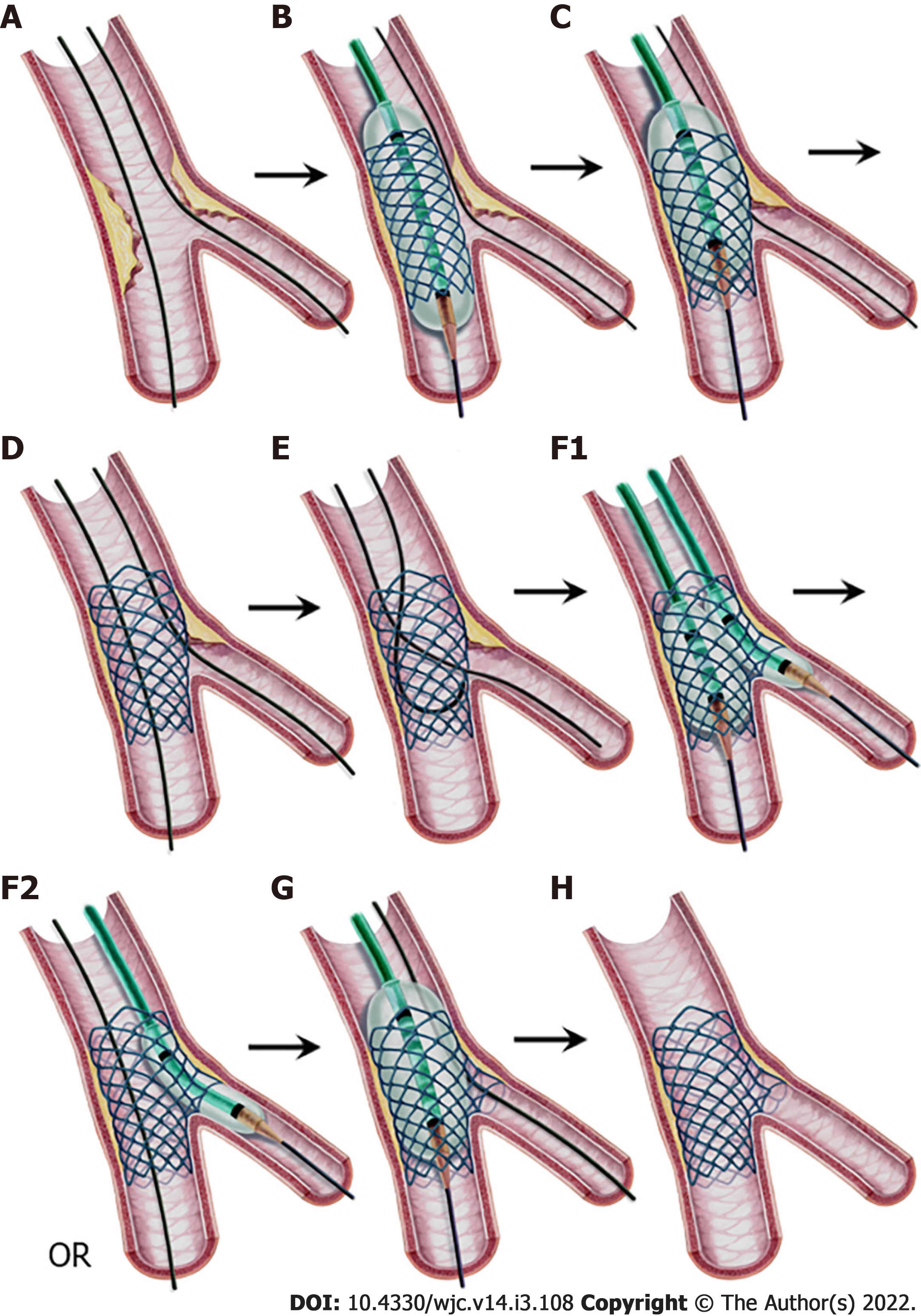
Figure 4 Provisional stenting technique, step-by-step.
A: Both branches are wired; B: A stent sized to the distal MV diameter is implanted in the MV; C: Proximal optimization technique (POT) application with a balloon sized to the proximal MV diameter with its distal shoulder aligned to the carina; D: Stent view after POT. If the result is satisfactory, stop here. If not, proceed to step E; E: Guidewire exchange; First, the SB is wired through the most distal cell. Second, the retracted and released SB wire is advanced into the distal MV as a “U” shape; F1: Kissing balloon inflation sized to branch diameters, or F2: SB ostium ballooning as a part of the POT-side-POT technique; G: Final POT; and H: Final result. MV: Main vessel; POT: Proximal optimization technique; SB: Side branch.
- Citation: Kırat T. Fundamentals of percutaneous coronary bifurcation interventions. World J Cardiol 2022; 14(3): 108-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v14/i3/108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.108