Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2021; 13(6): 163-169
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i6.163
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i6.163
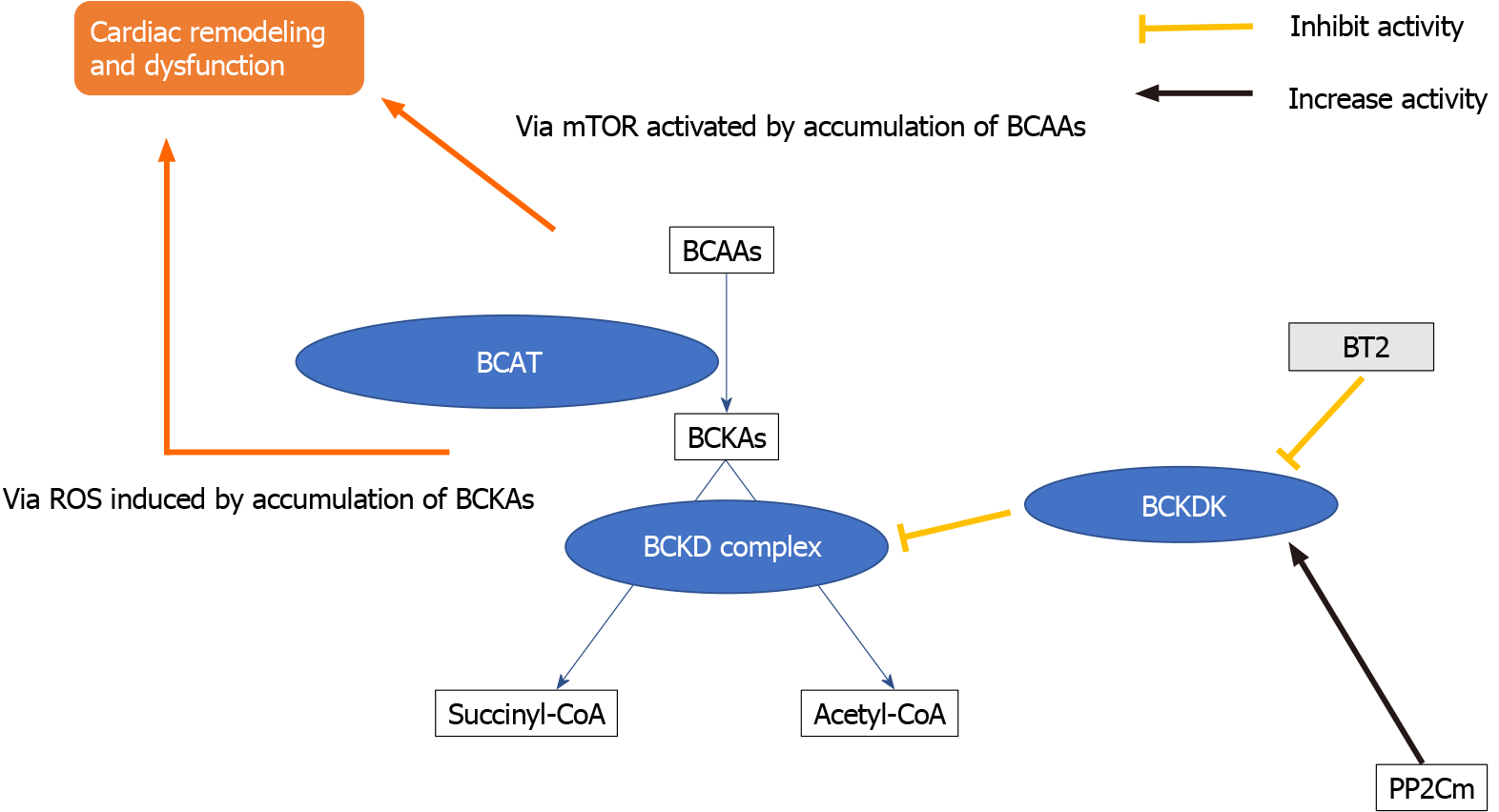
Figure 1 Branched-chain amino acid and its catabolic pathway in patients with heart failure.
Branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) are degraded into their final products of acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA, however the decrease of branched-chain keto acid (BCKA) dehydrogenase leads to the increase of BCKA. The increases of BCAAs and BCKAs potentially exacerbate heart failure. mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; BCAA: Branched-chain amino acid; BCKA: Branched-chain keto acid; BCAT: Branched chain aminotransferase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; BCKD: Branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase; BCKDK: Branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase kinase; BT2: 3,6-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid; PP2Cm: Protein phosphatase 2C in mitochondria.
- Citation: Narita K, Amiya E. Is branched-chain amino acid nutritional supplementation beneficial or detrimental in heart failure? World J Cardiol 2021; 13(6): 163-169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v13/i6/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v13.i6.163