Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2020; 12(7): 303-333
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i7.303
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i7.303
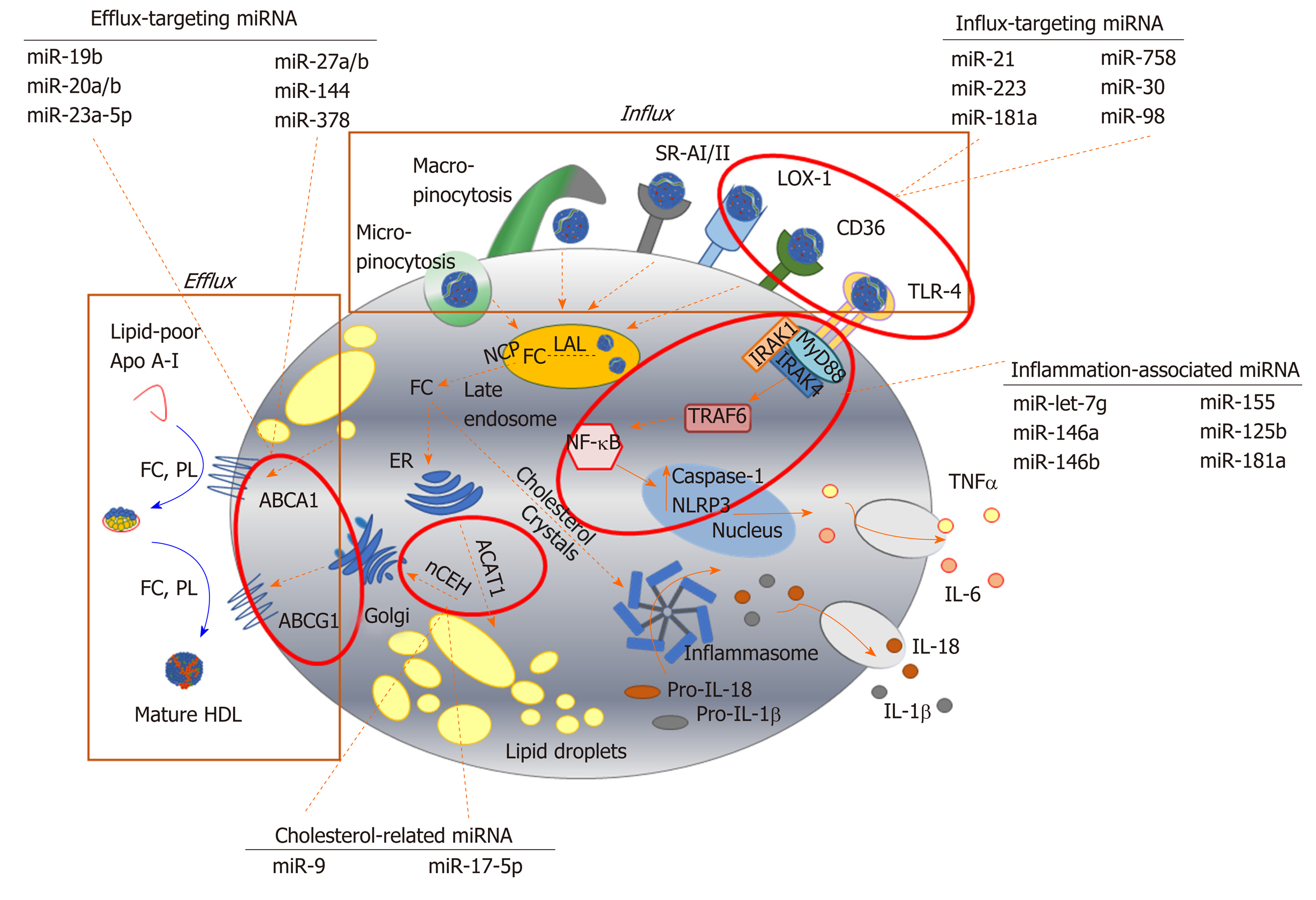
Figure 2 Key pathways involved in foam cell formation regulated by microRNA.
Native low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and oxidized LDL is processed in the late endosome/lysosomes by lysosomal acid lipase, generating free cholesterol which is stored in the form of lipid droplets after esterification via acyl-CoA cholesteryl acyl transferase or sterol O-acyltransferase 1 at the endoplasmic reticulum. Cholesterol can be removed from the cell by trafficking from the late endosomes, or by hydrolysis of lipid droplets and transport to the plasma membrane to be transferred to lipid-poor apolipoprotein A-I or nascent high-density lipoprotein via ABC transporters (ATP binding cassette transporter A1, ATP binding cassette transporter G1). Inflammatory signalling pathways can be activated in foam cells via recognition of oxLDL by toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), or by intracellular free cholesterol forming cholesterol crystals, leading to the expression and release of inflammatory cytokines. Since their initial discovery, numerous miRNA sequences have been shown to play a role in targeting each of these key steps in the formation of foam cells. For example, influx of modified lipoproteins into macrophages via oxidized low-density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1, cluster of differentiation 36 and TLR4, is reported to be regulated by miR-21, miR-30, miR-98, miR-181a, miR-223 and miR-758. The cholesterol efflux pathway is modulated by distinct sequences, including miR-19b, miR-20a/b, miR-23, miR-27a/b, mir-155 and miR-378, while miR-9 and miR-17 regulate the esterification and hydrolysis of cholesterol droplets. MicroRNA-181a regulates both lipid metabolism and inflammatory response, while let-7g, miR-146a/b, miR125b and miR-155 influence macrophage inflammatory phenotype. Dotted arrows indicate the paths for cholesterol derived from the extracellular environment within the macrophage; solid arrows indicate inflammatory signalling pathways. HDL: High density lipoprotein; ABCA1: ATP binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG1: ATP binding cassette transporter G1; ACAT-1: Acyl-CoA cholesteryl acyl transferase or sterol O-acyltransferase 1; ApoA-I: Apolipoprotein A-I; CD: Cluster of differentiation; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; FC: Free cholesterol; IL: Interleukin; IRAK: Interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 4; LAL: Lysosomal acid lipase; LOX-1: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; nCEH: Neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase; NPC: Niemann-Pick disease type C; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa beta; PL: Phospholipid; SR: Scavenger receptor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha.
- Citation: Lightbody RJ, Taylor JMW, Dempsie Y, Graham A. MicroRNA sequences modulating inflammation and lipid accumulation in macrophage “foam” cells: Implications for atherosclerosis. World J Cardiol 2020; 12(7): 303-333
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v12/i7/303.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v12.i7.303