Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2017; 8(2): 151-162
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
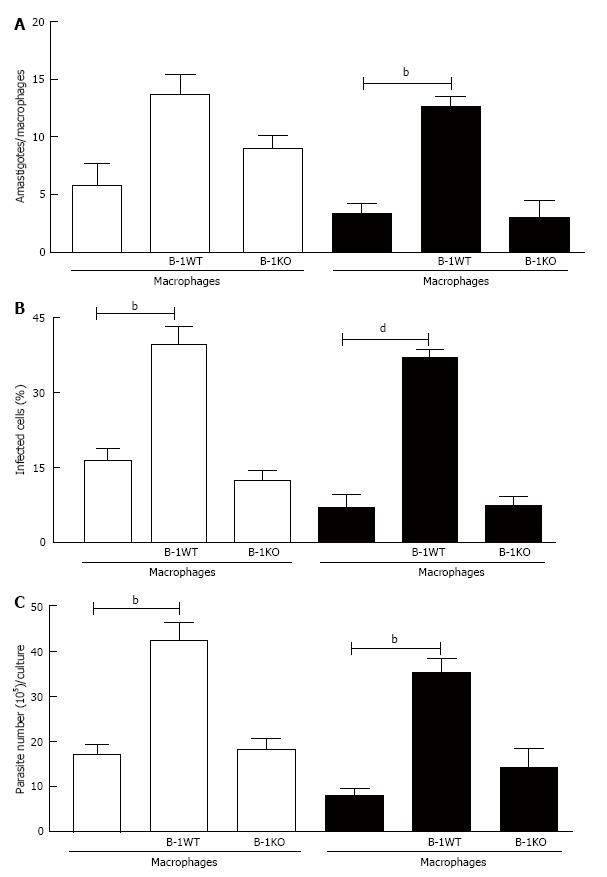
Figure 8 B-1 cells from interleukin-10 deficient mice are more competent to control Leishmania major infection in macrophages.
To confirm the production of IL-10 is involved in the susceptibility to infection by L. major, we used B-1 cells from BALB/c (white bars) and from IL-10 KO mice (black bars). Our data demonstrate decreased in the number of intracellular amastigotes (A) and percentage of infected cells (B). We also observed the significant decrease in the liberated promastigotes forms by infected macrophages co-cultured with B-1 cells from IL-10 KO mice (C). Statistical analysis was performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001.
- Citation: Arcanjo AF, Nunes MP, Silva-Junior EB, Leandro M, Rocha JDBD, Morrot A, Decote-Ricardo D, Freire-de-Lima CG. B-1 cells modulate the murine macrophage response to Leishmania major infection. World J Biol Chem 2017; 8(2): 151-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v8/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151