Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2017; 8(2): 151-162
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
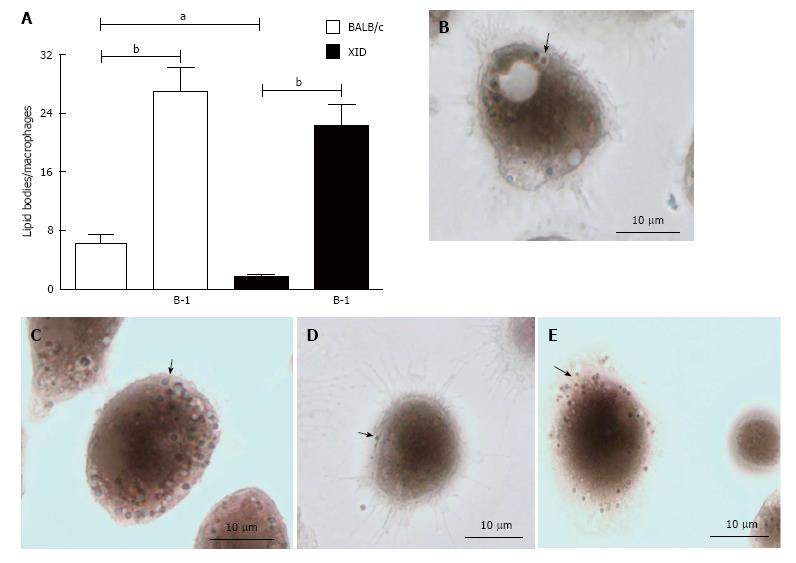
Figure 4 Presence of B-1 cells increased numbers of lipid bodies in infected macrophages.
Peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice were incubated with glass coverslips; some cultures were infected with L. major. Stained with Osmium tetroxide, the slides were washed and stained with DAPI (Sigma). The morphology of fixed cells was observed, and Nile red LBs were counted by light microscopy with a 100 × objective lens in 50 consecutively scanned leukocytes (A). Representative images of lipid body formation in infected macrophages from BALB/c mice (B), infected macrophages from BALB/c mice cultured in the presence of B-1 cells (C), infected macrophages from XID mice (D) and infected macrophages from XID mice co-cultured with B-1 cells (E). Black arrows pointing to the LB. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005.
- Citation: Arcanjo AF, Nunes MP, Silva-Junior EB, Leandro M, Rocha JDBD, Morrot A, Decote-Ricardo D, Freire-de-Lima CG. B-1 cells modulate the murine macrophage response to Leishmania major infection. World J Biol Chem 2017; 8(2): 151-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v8/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151