Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2017; 8(2): 151-162
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
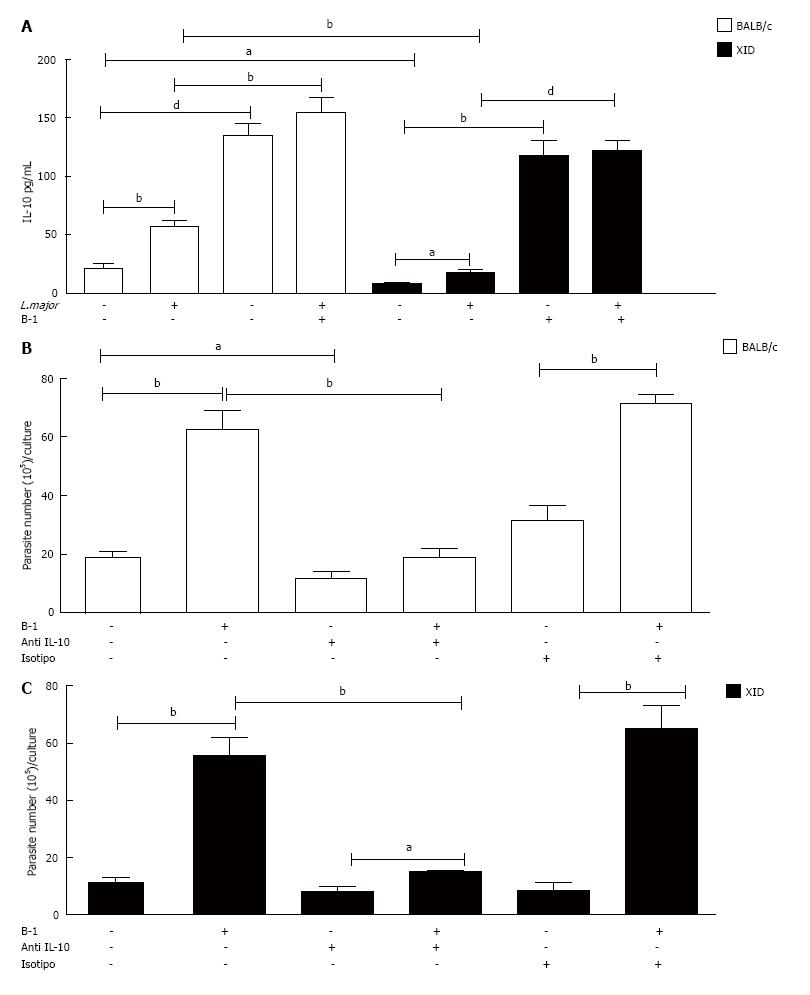
Figure 3 Interleukin-10 is a determinant factor for the increased parasite load in macrophages.
Peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice co-cultured with B-1 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of L. major (MOI 10:1). After 24 h, the supernatant was collected and IL-10 was measured by ELISA (A). All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Representative result of three different experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001. Co-cultures of B-1 cells and infected macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice were treated or not with doses of monoclonal neutralizing anti-IL-10 or control isotype. Once were infected with L. major, after 24 h, the cell cultures were washed with DMEM and incubated 3 d and then passed to Schneider medium. After 5 d in medium Schneider, promastigotes were counted in the supernatant (B). Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005.
- Citation: Arcanjo AF, Nunes MP, Silva-Junior EB, Leandro M, Rocha JDBD, Morrot A, Decote-Ricardo D, Freire-de-Lima CG. B-1 cells modulate the murine macrophage response to Leishmania major infection. World J Biol Chem 2017; 8(2): 151-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v8/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151