Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2017; 8(2): 138-150
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.138
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.138
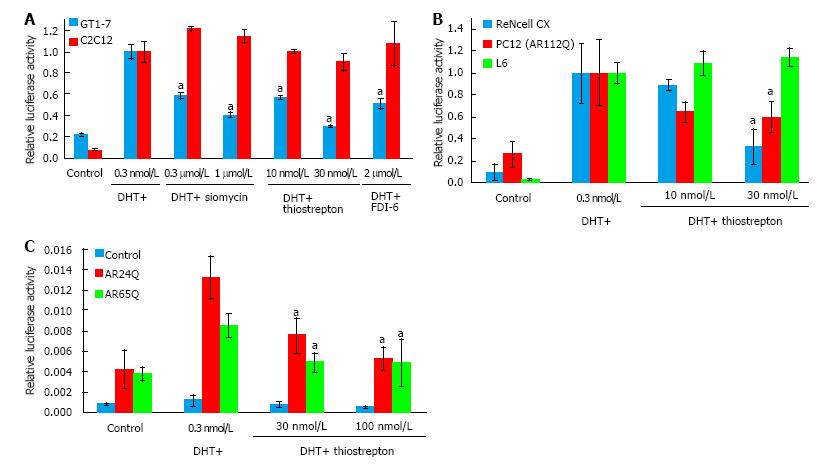
Figure 2 Thiazole antibiotics selectively inhibit androgen receptor in neuronal cells and have activity against polyQ-expanded androgen receptor.
A: GT1-7 and C2C12 cells were transfected with androgen-responsive and control luciferase reporters and treated with the indicated drugs overnight. Both thiazole antibiotics siomycin and thiostrepton, as well as the selective FOXM1 inhibitor FDI-6, inhibited AR activity in GT1-7 but not C2C12 cells, with thiostrepton being the most potent of the drugs; B: Rat L6 skeletal muscle cells and ReNcell CX and PC12 (ARQ112) neuronal cells were transfected with androgen-responsive and control luciferase reporters and treated with thiostrepton overnight. Thiostrepton inhibited AR luciferase activity in neuronal, but not muscle cells; C: 293 cells were transfected with androgen-responsive and control luciferase reporters as well as plasmids containing AR with 24 (normal state) or 65 (disease state) glutamines and treated with drugs mentioned above overnight. Both normal and disease state AR activity was reduced by thiostrepton treatment. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM, aP < 0.05. AR: Androgen receptor.
- Citation: Otto-Duessel M, Tew BY, Vonderfecht S, Moore R, Jones JO. Identification of neuron selective androgen receptor inhibitors. World J Biol Chem 2017; 8(2): 138-150
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v8/i2/138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.138