Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2016; 7(3): 223-230
Published online Aug 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i3.223
Published online Aug 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i3.223
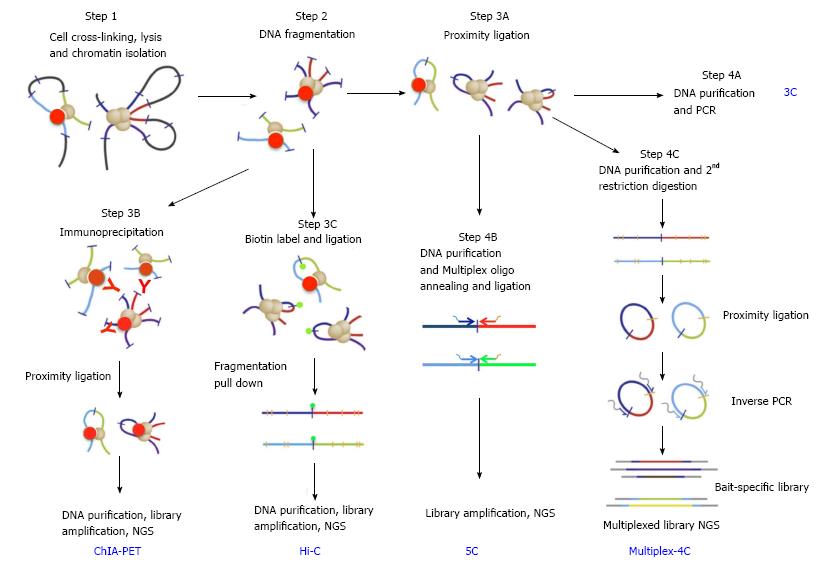
Figure 2 Key steps in chromosomal conformation capture protocols (adapted from Stadhouders et al[46], 2013).
Bold blue upper case letters denote capture protocols and black lower case phrases denote the key steps. Steps 1 and 2 (cell crosslinking, chromatin preparation and fragmentation) are common to all capture protocols. Following these, the ends of captured DNA fragments are ligated under highly diluted condition (step 3A, proximity ligation), and junctions of captured DNAs are detected by PCR using pray- and bait-specific primers (step 4A, 3C). Alternatively, capture events can be selected by immunoprecipitation using antibody against specific architectural proteins (step 3B for ChIA-PET). Capture events can be also enriched by pull-down of Biotin-labeled ligation junction (step 3C for Hi-C). After purification, libraries of junction DNAs are amplified and sequenced by next-generation-sequencing (NGS). After step 3A, library of bait- and pray-specific primers can be used in conjunction (step 4B for 5C) to generate libraries of selected capture junctions for NGS sequencing. Bait-specific primers can also be used to generate a capture library (step 4C for 4C or multiplex 4C).
- Citation: Ma Z, Li M, Roy S, Liu KJ, Romine ML, Lane DC, Patel SK, Cai HN. Chromatin boundary elements organize genomic architecture and developmental gene regulation in Drosophila Hox clusters. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(3): 223-230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i3/223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i3.223