Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 178-187
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178
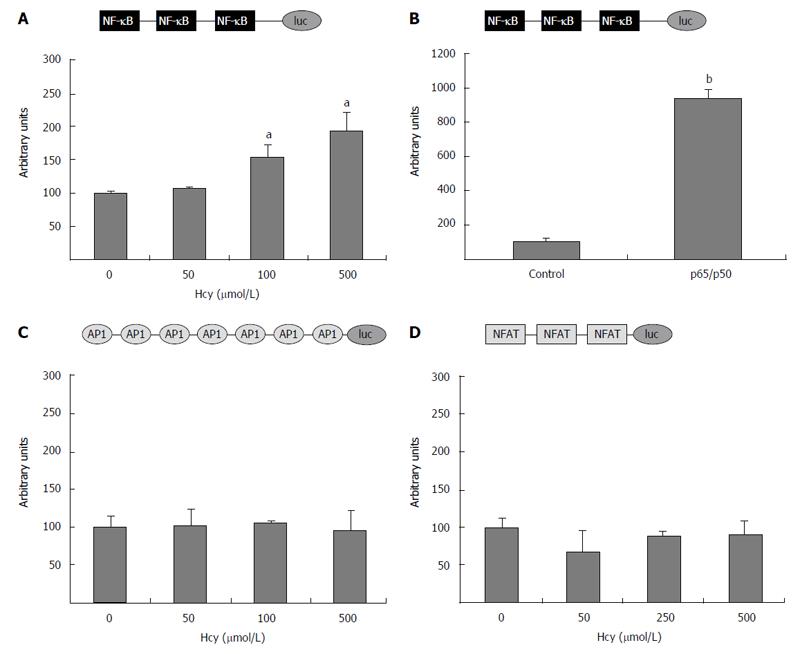
Figure 5 Homocysteine activates nuclear factor kappa B, but has no effect on activator protein-1 or nuclear factor of activated T cells activity.
HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with (NF-κB)3-luc construct (A), (AP-1)7-luc (C), or (NFAT)3-luc (D) and exposed to homocysteine (50-500 μmol/L). For positive control, the cells were co-transfected with (NF-κB)3-luc and the vector for the heterodimer p65/50. The activity of the luciferase reporter driven by the corresponding promoter was normalized to the co-transfected β-galactosidase. Treatment with high concentrations of homocysteine (250 and 500 μmol/L) significantly increased (aP < 0.05) the activity of the promoter containing the three NF-κB binding sites, while no effect of Hcy (P > 0.05) was observed on promoters containing binding sites for AP-1 (C) or NFAT (D). The activity of the (NF-κB)3-luc construct was greatly enhanced by p65/p50 overexpression, used as positive control (bP < 0.001). NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; AP-1: Activator protein-1; NFAT: Nuclear factor of activated T cells; Hcy: Homocysteine.
- Citation: Trusca VG, Mihai AD, Fuior EV, Fenyo IM, Gafencu AV. High levels of homocysteine downregulate apolipoprotein E expression via nuclear factor kappa B. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 178-187
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/178.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178