Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 178-187
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178
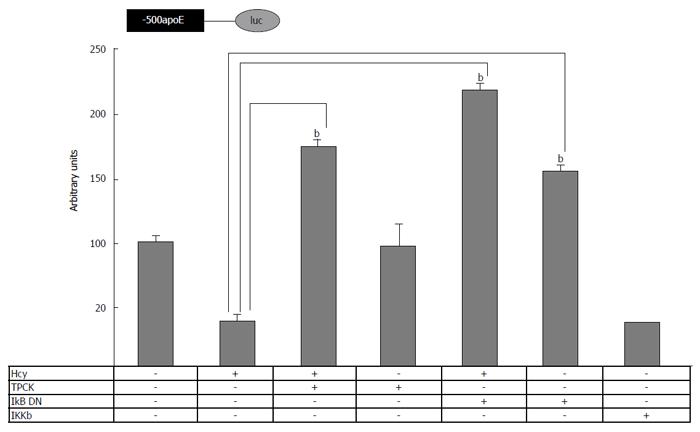
Figure 4 Involvement of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in homocysteine-mediated inhibition of apolipoprotein E promoter activity.
HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids containing apoE proximal promoter in the presence of homocysteine, TPCK or expression vectors for IKβ dominant negative (IKβ DN) or IKKβ. The activity of the luciferase reporter, normalized to the co-transfected β-galactosidase, was significantly reduced (P < 0.05) by IKKβ overexpression, similarly to Hcy treatment. TPCK (NF-κB inhibitor) as well as IKβ DN overexpression abrogated the inhibitory effect of homocysteine on apoE promoter activity, bP < 0.001. NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TPCK: N-p-Tosyl-L-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketone; Hcy: Homocysteine; IKKβ: IκB kinase β; ApoE: Apolipoprotein E.
- Citation: Trusca VG, Mihai AD, Fuior EV, Fenyo IM, Gafencu AV. High levels of homocysteine downregulate apolipoprotein E expression via nuclear factor kappa B. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 178-187
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/178.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178