Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 178-187
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178
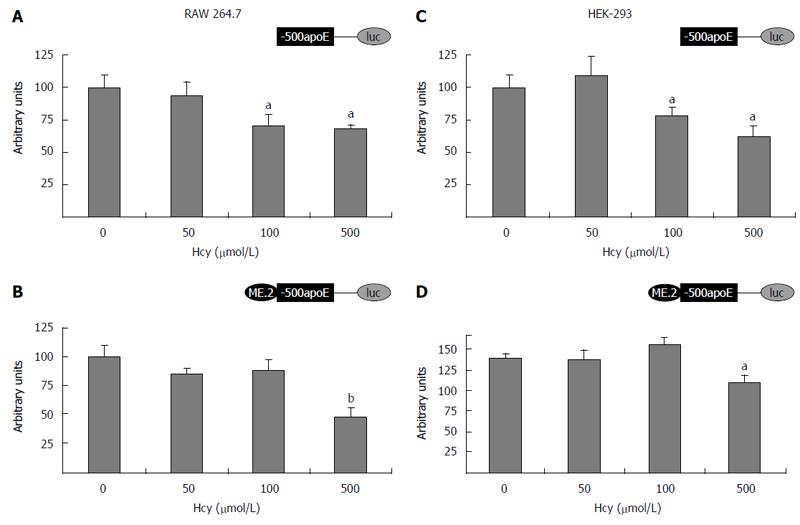
Figure 2 Homocysteine inhibits the activity of apolipoprotein E proximal promoter in either absence or presence of ME2 in RAW 264.
7 macrophages and HEK-293 cells. Transient transfection experiments were performed using (-500/+73) apoE proximal promoter (A, C) or ME2/(-500/+73) multienhancer/apoE promoter constructs (B, D) driving the luciferase reporter and the transfected cells were incubated with 50-500 μmol/L homocysteine for 24 h. Then, luciferase activity was assessed and normalized to the activity of the co-transfected β-galactosidase. Treatment of RAW 264.7 (A, B) and HEK-293 cells (C, D) with 500 μmol/L Hcy significantly decreased (aP < 0.05 or bP< 0.01) apoE promoter activity, in the presence (B, D) or in the absence of ME2 (A, C). Low concentrations of Hcy (50 μmol/L) did not considerably decrease (P > 0.05) the activity of apoE promoter either in the absence (A, C) or in the presence of ME2 (B, D). MEK1/2: MAPK/ERK kinase; Hcy: Homocysteine; ApoE: Apolipoprotein E.
- Citation: Trusca VG, Mihai AD, Fuior EV, Fenyo IM, Gafencu AV. High levels of homocysteine downregulate apolipoprotein E expression via nuclear factor kappa B. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 178-187
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/178.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.178