Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 128-137
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.128
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.128
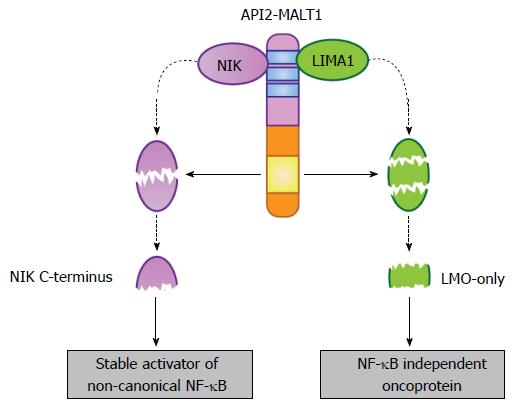
Figure 4 Selective substrates of the API2-mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 fusion oncoprotein.
The API2 moiety recruits at least two proteins (NIK and LIMA1), making them available as targets for the MALT1 protease domain (yellow box) preserved in the MALT1 moiety. In the case of NIK, site-specific cleavage frees a stable, catalytically active fragment that promotes deregulated non-canonical NF-κB activation. This fragment is stable because it lacks the C-terminal domains necessary for its recruitment to the NIK “destruction complex”. In the case of LIMA1, site-specific cleavage at two sites not only destroys the tumor suppressor function of the full-length LIMA1 protein but also liberates a central, LMO-domain only fragment that displays gain-of-function oncogenic activity. MALT: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NIK: NF-κB inducing kinase; LIMA: LIM domain and actin-binding protein 1.
- Citation: Rosebeck S, Lim MS, Elenitoba-Johnson KSJ, McAllister-Lucas LM, Lucas PC. API2-MALT1 oncoprotein promotes lymphomagenesis via unique program of substrate ubiquitination and proteolysis. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 128-137
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/128.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.128