Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 128-137
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.128
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.128
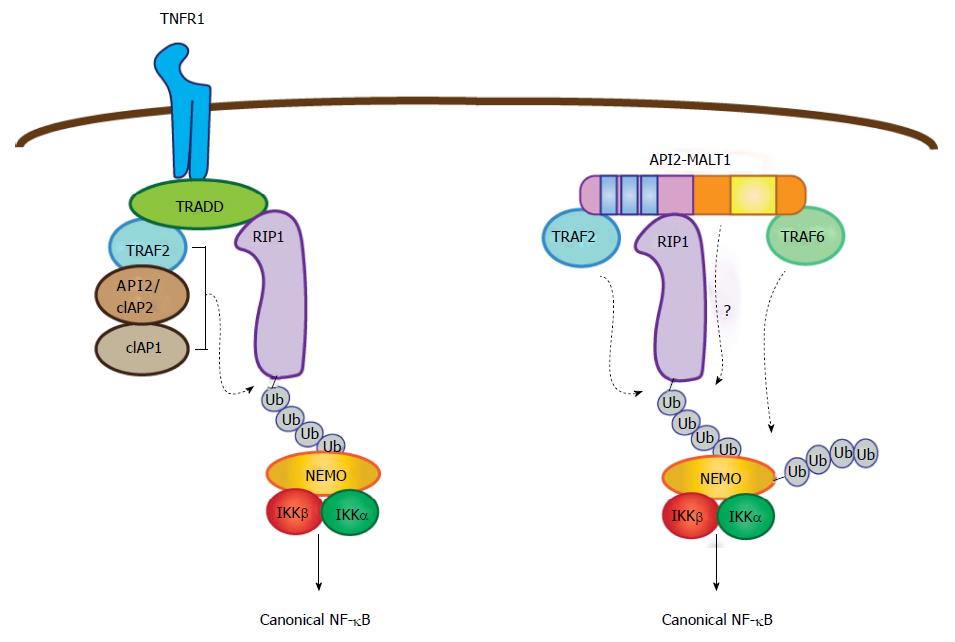
Figure 3 Parallel pathways for canonical nuclear factor-κB activation mediated by tumor necrosis factor receptor and API2-mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1.
In the context of TNF receptor activation, TNF receptor associated death domain protein brokers the assembly of a complex containing three E3 ubiquitin ligases (API2/cIAP2, cIAP1, and TRAF2), which together promote RIP1 ubiquitination. This then serves as a platform for recruitment of NEMO. In parallel fashion, the API2 moiety of API2-MALT1 binds TRAF2 and RIP1 to promote RIP1 ubiquitination, but in this case the ubiquitination event seems to be mediated only by TRAF2. Importantly, the MALT1 moiety facilitates the ubiquitination of RIP1 through an as of yet undefined mechanism. Recruitment of NEMO via the RIP1 ubiquitin scaffold allows MALT1 moiety-associated TRAF6 to promote NEMO ubiquitination, IKK complex activation and subsequent canonical NF-κB activation. TRAF: TNF receptor associated factor; NEMO: NF-κB essential modulator; RIP1: Receptor interacting protein 1; TRADD: TNF receptor associated death domain protein; IKK: IκB kinase; MALT: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Rosebeck S, Lim MS, Elenitoba-Johnson KSJ, McAllister-Lucas LM, Lucas PC. API2-MALT1 oncoprotein promotes lymphomagenesis via unique program of substrate ubiquitination and proteolysis. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 128-137
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/128.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.128