Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 379-388
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.379
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.379
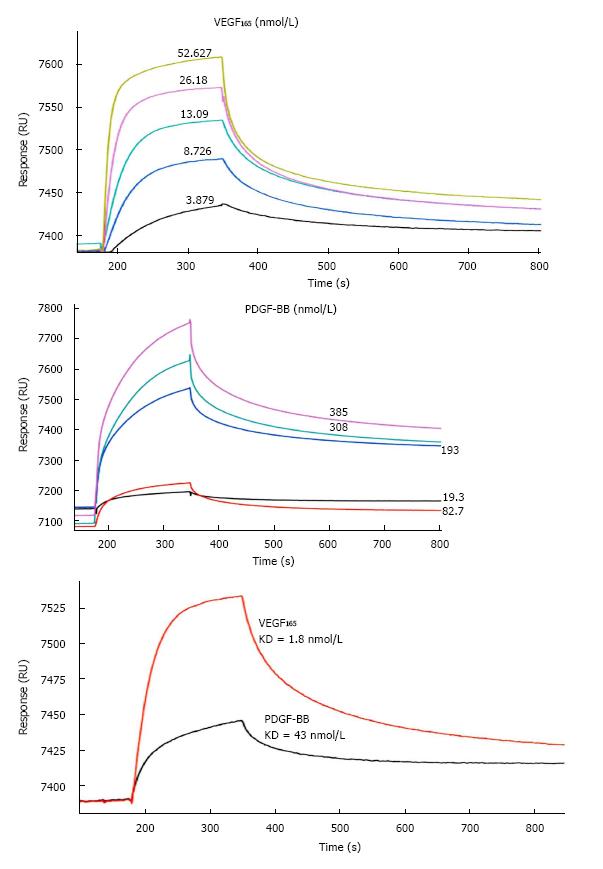
Figure 2 Quantitative measurement of connective tissue growth factor binding to vascular endothelial growth factor 165 and platelet-derived growth factor-BB in surface plasma resonance analysis.
The binding kinetics of CTGF to VEGF165 (A) or to PDGF-BB (B) were determined by injecting VEGF165 ranging from 3.879 nmol/L to 52.267 nmol/L or PDGF-BB ranging 19.3 nmol/L to 385 nmol/L over CTGF immobilized channel and reference channel at 30 μL/min for 3 min simultaneously. The reference sensorgram has already deducted to eliminate the signal from a bulk refractive index shift; C: Sensorgrams of SPR analysis showed that the equilibrium dissociation constant for CTGF binding to PDGF-BB or VEGF165 was 43 nmol/L or 1.8 nmol/L respectively. CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF-B: Platelet-derived growth factor-B; SPR: Surface plasma resonance.
- Citation: Pi L, Chung PY, Sriram S, Rahman MM, Song WY, Scott EW, Petersen BE, Schultz GS. Connective tissue growth factor differentially binds to members of the cystine knot superfamily and potentiates platelet-derived growth factor-B signaling in rabbit corneal fibroblast cells. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 379-388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.379