Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 358-365
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.358
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.358
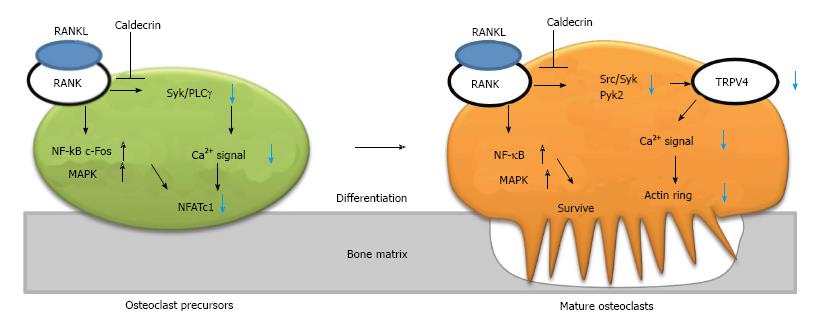
Figure 3 Caldecrin suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption.
RANKL binds to its receptor (RANK) on the osteoclast precursor, leading to simultaneous activation of two pathways: the NF-κB/ MAPK/c-Fos axis and the Syk/PLCγ-calcium oscillation- NFATc1 axis. In mature osteoclasts, RANKL also activates the NF-κB/MAPK and Src/Syk/Pyk2-TRPV4 channel–calcium entry–actin ring formation axes. Caldecrin inhibits the latter pathways (but not the NF-κB/MAPK pathway) in the precursor and mature osteoclasts. TRPV4: Transient receptor potential vanilloid channel 4; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; RANKL: RANK ligand; PLCγ: Phospholipase Cγ; Pyk2: Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2; NFATc1: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; Syk: Spleen tyrosine kinase.
- Citation: Tomomura M, Tomomura A. Caldecrin: A pancreas-derived hypocalcemic factor, regulates osteoclast formation and function. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 358-365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/358.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.358