Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2015; 6(3): 71-77
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.71
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.71
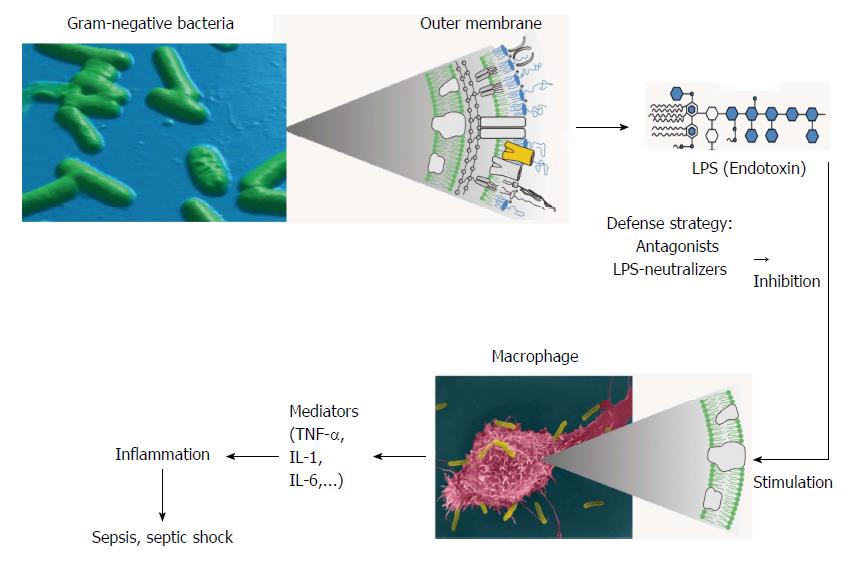
Figure 2 Mechanisms of lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine (mediator) secretion with subsequent induction of inflammation and sepsis.
Without therapeutical intervention, the interaction of the toxins leads to cell activation with subsequent release of inflammation-inducing compounds eventually resulting in sepsis. Intervention strategies may be performed by e.g., AMP and LPS/LP-neutralizers. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Brandenburg K, Schürholz T. Lack of new antiinfective agents: Passing into the pre-antibiotic age? World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(3): 71-77
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i3/71.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.71