Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2015; 6(3): 249-264
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.249
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.249
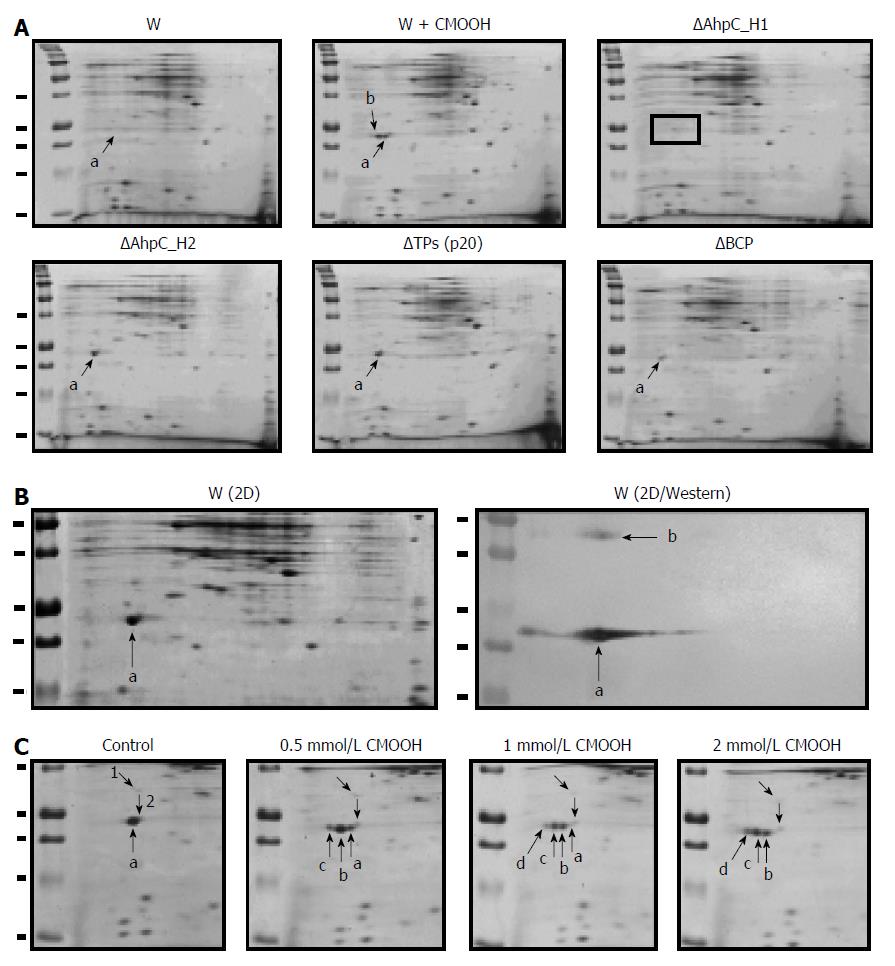
Figure 9 Expression of peroxiredoxins in the wild-type and Prx-deficient B.
subtilis strains. A: Two-dimensional (2D) electrophoresis of soluble proteins from untreated (W) and cumene hydroperoxide (CMOOH)-treated (W + CMOOH) wild-type B. subtilis, and Prx-null mutant strains. Soluble protein fraction (20 μg) obtained from exponential B. subtilis cultures treated with or without 1 mM CMOOH for 30 min was separated in 2D gels and analyzed for AhpC_H1 expression after staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. a indicates AhpC_H1; b indicates AhpC_H1 shift to acidic area; in AhpC_H1 deletion mutant (ΔAhpC_H1), AhpC_H1-specific signal is absent; B: B. subtilis was grown and treated as in (A), and soluble proteins (1 μg) were separated by 2D electrophoresis and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (W/2D) or analyzed by western blotting using polyclonal antibodies against AhpC_H1 (2D/Western); a and b indicate the position of AhpC_H1 monomeric and dimeric forms, respectively; C: B. subtilis cultures were grown as in (A), treated with the indicated concentrations of CMOOH for 30 min, and soluble proteins were separated by 2D electrophoresis followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. a, indicates original and b, c, and d indicate oxidized AhpC_H1 proteins; 1 and 2 denote internal standards. 2D electrophoresis was performed using 4-7 pH gradients (left to right); molecular weight markers (50, 37, 25, 20, and 15 kDa) are shown in the left lines.
-
Citation: Cha MK, Bae YJ, Kim KJ, Park BJ, Kim IH. Characterization of two alkyl hydroperoxide reductase C homologs alkyl hydroperoxide reductase C_H1 and alkyl hydroperoxide reductase C_H2 in
Bacillus subtilis . World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(3): 249-264 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i3/249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.249