Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2015; 6(3): 249-264
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.249
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.249
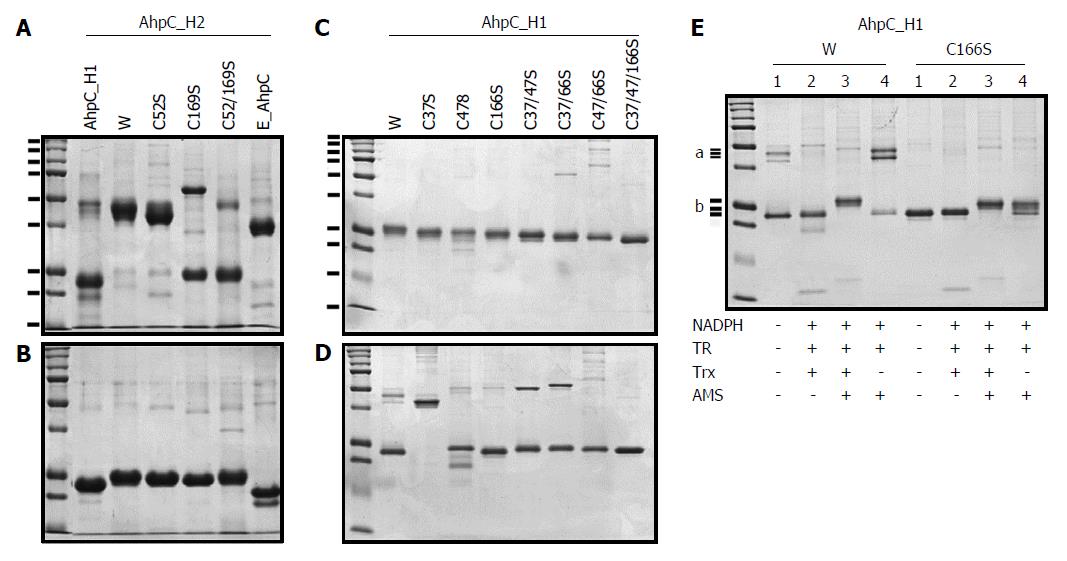
Figure 2 SDS-PAGE analyses of AhpC_H1 and AhpC_H2 proteins and their mutants carrying Cys→Ser substitutions.
The wild-type (lane W) and mutated AhpC_H2 and AhpC_H1, and E. coli AhpC proteins were separated in non-reducing (A) and reducing (B) 12% SDS-PAGE gels; first lanes show molecular weight markers (15, 20, 25, 37, 50, 75, 100, 150, and 250 kDa). TCEP/AMS-treated (C) and non-treated (D) wild-type (lane W) and mutated AhpC_H1 proteins were separated in non-reducing 14% SDS-PAGE gels. AhpC_H1 and its C166S mutant reduced or not with the Trx system containing Trx 1, Trx reductase (TR), and NADPH were modified with a sulfhydryl group-specific reagent AMS and separated in non-reducing 14% SDS-PAGE gels (E). a marks the position of a single AhpC_H1 band (W, lane 1) and double bands (W, lane 4). b marks three positions of the AhpC_H1 band after the treatments indicated at the bottom. First lanes in B1, B2, and C show molecular weight markers (10, 15, 20, 25, 37, 50, 75, 100, 150, 250 kDa).
-
Citation: Cha MK, Bae YJ, Kim KJ, Park BJ, Kim IH. Characterization of two alkyl hydroperoxide reductase C homologs alkyl hydroperoxide reductase C_H1 and alkyl hydroperoxide reductase C_H2 in
Bacillus subtilis . World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(3): 249-264 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i3/249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.249