Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2014; 5(4): 437-456
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i4.437
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i4.437
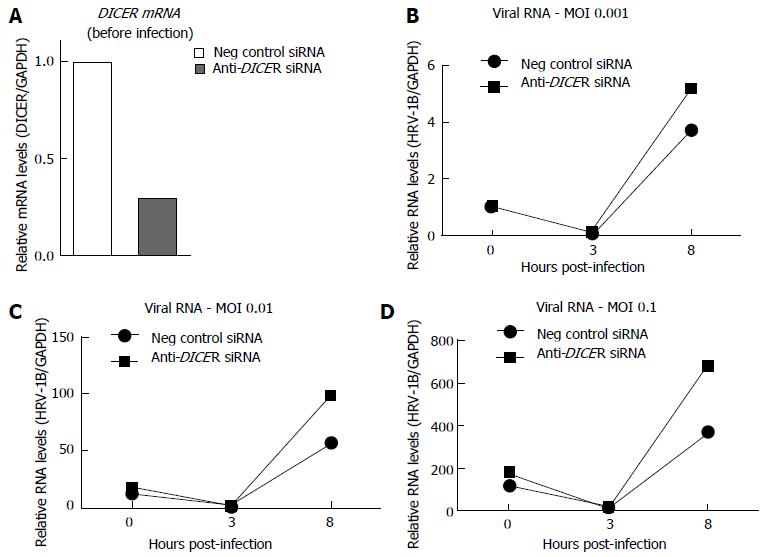
Figure 2 Prolonged DICER knock-down enhanced human rhinovirus-1B replication (preliminary experiments).
BEAS-2B cells were transfected for three rounds with either a negative control siRNA or anti-DICER siRNA. Forty-eight hours after the third transfection, cells were infected with the indicated amount of HRV-1B, expressed as MOI (multiplicity of infection). Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to quantify (A) DICER mRNA levels before infection or (B-D) HRV-1B RNA at 0, 3 or 8 h post-infection (HPI). The plotted values represent the average of qPCR duplicates from one experiment. The 0 HPI sample at MOI 0.001 was used as calibrator for all samples.
- Citation: Bondanese VP, Francisco-Garcia A, Bedke N, Davies DE, Sanchez-Elsner T. Identification of host miRNAs that may limit human rhinovirus replication. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(4): 437-456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i4/437.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i4.437