Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 254-268
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.254
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.254
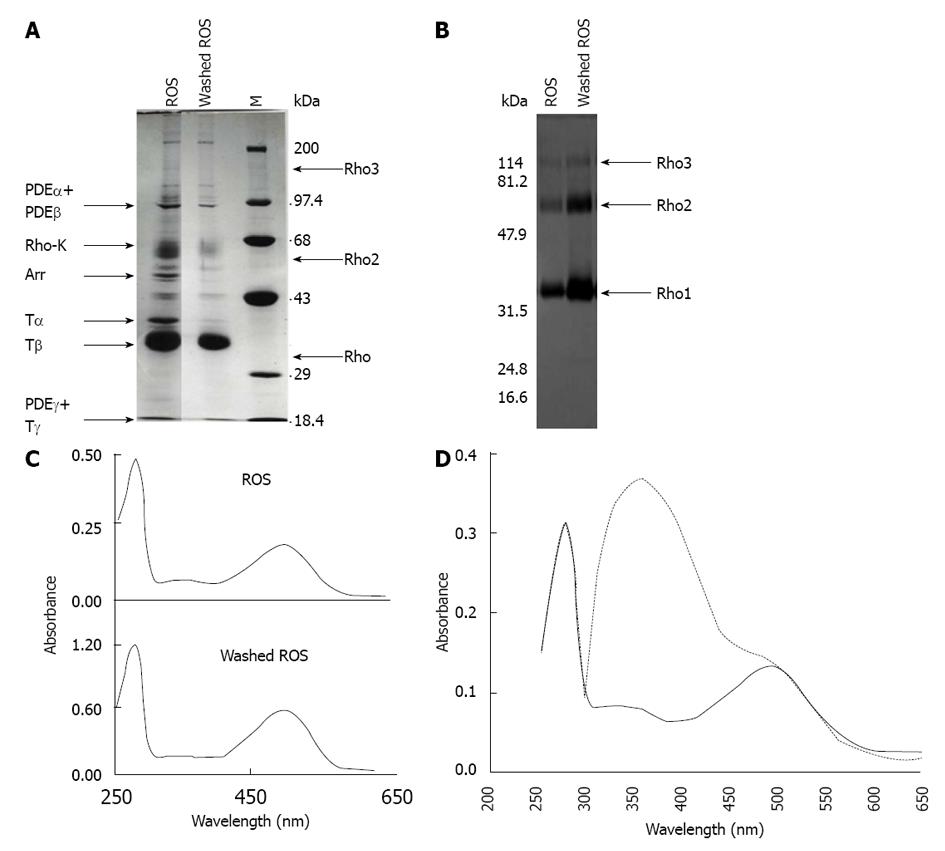
Figure 2 Isolation of rod outer segments, preparation of washed rod outer segments membranes, and reconstitution of rhodopsin.
A: ROS were isolated from frozen bovine retinas and were hypotonically washed in the dark until no peripheral proteins were released. Arrows indicate the migration of rhodopsin (Rho), rhodopsin oligomers (Rho2 and Rho3), α-, β- and γ-subunits of the cGMP phosphodiesterase PDE6 (PDEα, PDEβ and PDEγ), α-, β- and γ-subunits of transducin (Tα, Tβ and Tγ), rhodopsin kinase (Rho-K), and arrestin-1 (Arr); B: ROS and dark-depleted ROS membranes were separated by SDS-PAGE, electrotransferred to a nitrocellulose filter and analyzed using polyclonal anti-rhodopsin antibodies. Arrows point out the migration of rhodopsin (Rho), rhodopsin dimers (Rho2), and rhodopsin trimers (Rho3). C: Absorption spectra of solubilized ROS and washed-ROS membranes in the dark; D: Regeneration of rhodopsin. A sample of depleted ROS membranes was bleached with hydroxylamine and incubated with an excess of 11-cis-retinal. Shown is the UV/visible spectra of rhodopsin in the dark, before (dashed line) and after (continuous line) removing the excess of 11-cis-retinal by washing with BSA. M: Molecular weight markers; ROS: Rod outer segments.
- Citation: Araujo NA, Sanz-Rodríguez CE, Bubis J. Binding of rhodopsin and rhodopsin analogues to transducin, rhodopsin kinase and arrestin-1. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 254-268
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.254