Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 240-253
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.240
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.240
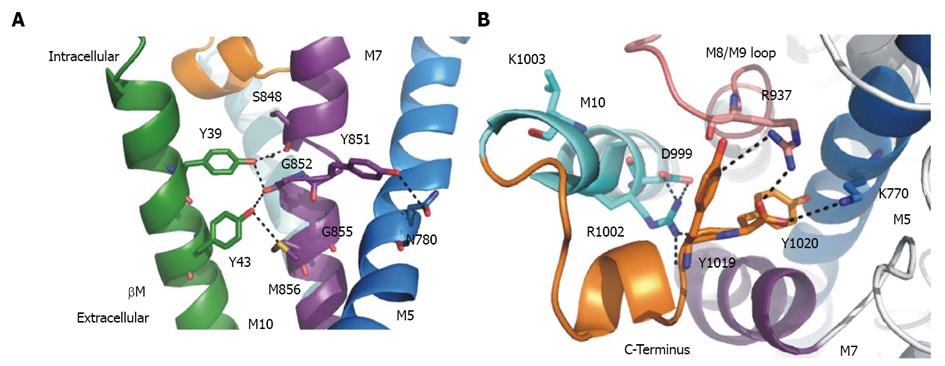
Figure 7 Structural details of the C-terminal region and α/β-interactions.
A: Structural details (PDB structure entry 3B8E) of putative interactions between the α- and β-subunit. Interacting residues are shown as sticks. Tyr39 and Tyr43 in the β-transmembrane domain (green) can interact with αM7 (purple). The α-helix is unwound at residue Gly952 (αM7). Tyr851 can form hydrogen bonds to Asn780 in αM5 (marine), which is part of the K+ binding site I and II. Also shown is αM10 (light blue) with the C-terminus (orange) of the α-subunit; B: Structural details of the C-terminal region viewed from the intracellular side. Possibly interacting residues are shown in sticks. The C-terminal Tyr1019 and Tyr1020 (orange) can interact with Arg1002 in αM10 (light blue), Arg937 (αM8/M9-loop in purple) and Lys770 in αM5 (marine). Asp999 (αM10) can form hydrogen bonds to Arg1002. Lys1003 (αM10) is not involved in the C-terminal network.
- Citation: Spiller S, Friedrich T. Functional analysis of human Na+/K+-ATPase familial or sporadic hemiplegic migraine mutations expressed in Xenopus oocytes. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 240-253
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.240