Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 224-230
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.224
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.224
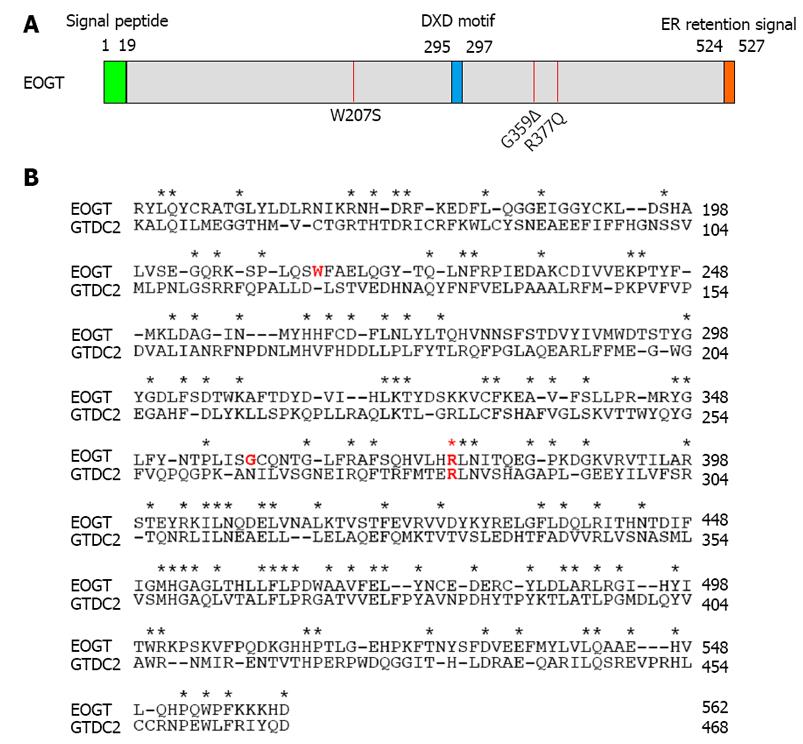
Figure 2 Extracellular O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine mutations found in Adams-Oliver syndrome.
A: A schematic representation of the primary structure of EOGT. The amino-terminal signal peptide is shown in yellow and the carboxyl-terminal Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retrieval signal is in orange. The putative DXD motif involved in binding the nucleotide sugar is shown in blue. The position of each mutation is indicated by a red line; B: The amino acid sequence alignment of mouse EOGT (NP_780522, 149-562 aa) and mouse GTDC2/EOGT-L (Q8BW41, 55-468 aa). Identical amino acid residues are indicated by asterisks. Amino acid residues corresponding to the mutations in patients with Adams-Oliver syndrome are highlighted by red letters. EOGT: Extracellular O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine.
-
Citation: Ogawa M, Furukawa K, Okajima T. Extracellular
O -linked β-N -acetylglucosamine: Its biology and relationship to human disease. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 224-230 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.224