Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 115-129
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.115
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.115
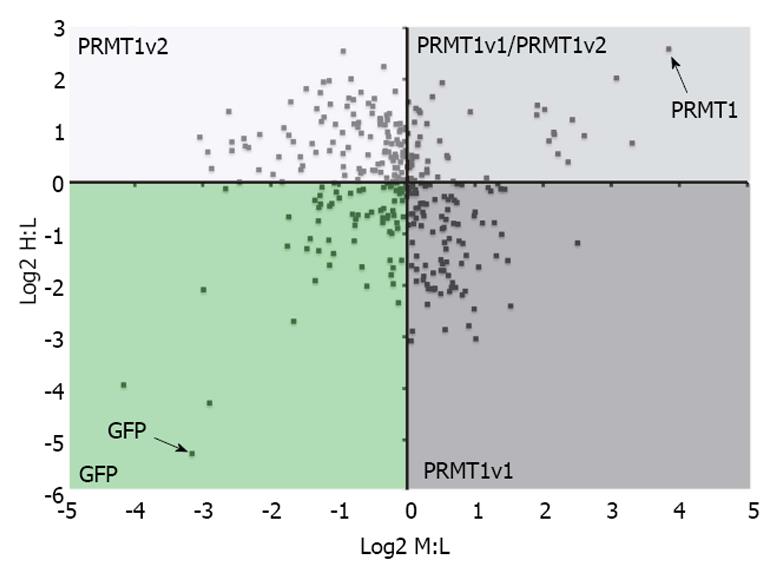
Figure 3 Protein arginine methyltransferase 1v1 and protein arginine methyltransferase 1v2 have potentially different interacting protein profiles.
Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) and mass spectrometry was used to identify protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 1v1 protein binding partners and PRMT1v2 protein binding partners. Cells stably expressing GFP alone, GFP-tagged PRMT1v1 or GFP-tagged PRMT1v2 were grown independently in media containing light (L), medium (M) and heavy (H) isotopes of arginine and lysine residues, respectively. Protein lysates were collected, immunoprecipitated for GFP (isolation of PRMT1v1 and PRMT1v2 interacting protein), and subjected to mass spectrometry for peptide identification. The Log2 of the SILAC ratios for the peptides identified from this experiment are plotted on the scatter plot. The x-axis is the Log2 of the H:L SILAC ratio or PRMT1v2 interacting proteins. The y-axis is the Log2 of the M:L SILAC ratio or PRMT1v1 interacting proteins. Each data point represents a single protein that was identified in this experiment. The greater this ratio is for a protein, the higher the probability of the interaction being real. This revealed a protein interacting profile identifying PRMT1v1-specific interacting proteins (PRMT1v1 quadrant), PRMT1v2-specific interacting proteins (PRMT1v2 quadrant) and common interacting proteins (PRMT1v1/PRMT1v2 quadrant; unpublished data). These results require further validation.
- Citation: Baldwin RM, Morettin A, Côté J. Role of PRMTs in cancer: Could minor isoforms be leaving a mark? World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 115-129
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.115