Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2013; 4(2): 18-29
Published online May 26, 2013. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v4.i2.18
Published online May 26, 2013. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v4.i2.18
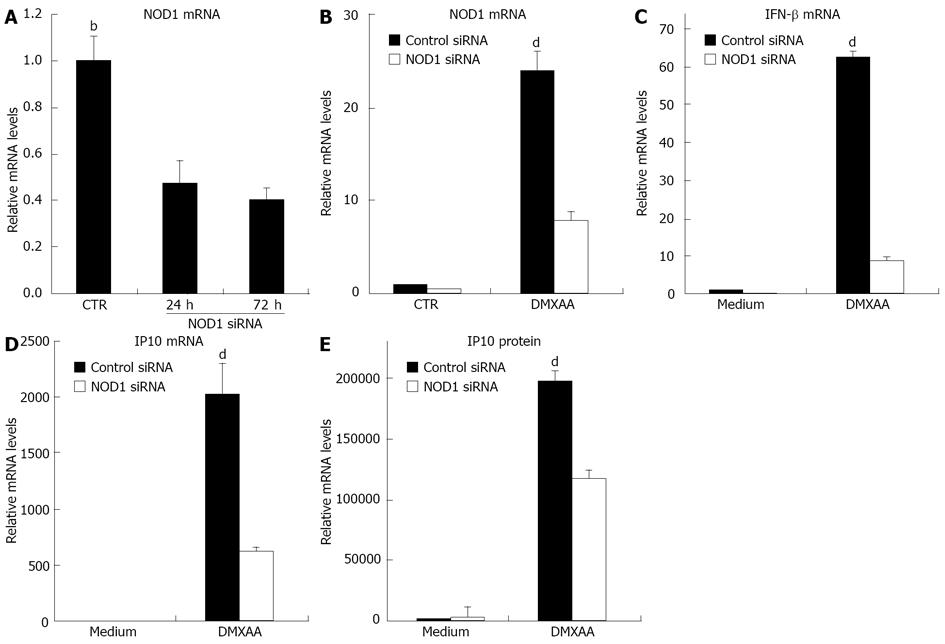
Figure 5 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid-induced interferon-β expression inhibited by nucleotide oligomerization domain 1 small interfering RNA.
A: C10 cells were transfected with control small interfering RNA (siRNA) or nucleotide oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1) siRNA. Total RNA was extracted at indicated time points and the relative NOD1 mRNA levels were measured by real time real time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). After transfected with control siRNA or NOD1 siRNA for 72 h, C10 cells were further incubated with or without 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid 100 μg/mL for 6 h; B-E: The relative NOD1, interferon (IFN)-β and inducible protein-10 (IP10) mRNA levels were measured by real time RT-PCR or the supernatants were removed and IP10 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (bP < 0.01 vs 24 h or 72 h; dP < 0.01 vs NOD1 siRNA, data are shown as the mean ± SE).
- Citation: Yu Z, Predina JD, Cheng G. Refractoriness of interferon-beta signaling through NOD1 pathway in mouse respiratory epithelial cells using the anticancer xanthone compound. World J Biol Chem 2013; 4(2): 18-29
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v4/i2/18.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v4.i2.18