Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2012; 3(2): 34-40
Published online Feb 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i2.34
Published online Feb 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i2.34
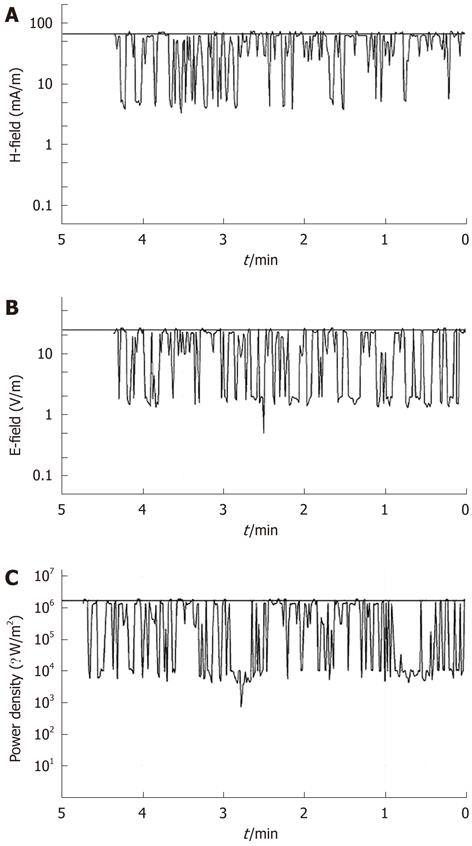
Figure 1 A time analysis of the electromagnetic field measured by a Narda SRM-3000 around 1760 MHz during exposure at 3 cm from the antenna of a mobile phone with specific absorption rate = 0.
086 W/Kg. Cell cultures were placed at 3 cm from the antenna of the mobile phone. A: Time analysis of the H field component around 1760 MHz during exposure, whose intensity remained < 66 mA/m; B: Time analysis of the E field component at the frequency of 1760 MHz, provided during exposure. Its intensity did not exceed 25 V/m; C: Time analysis of the power density of the electromagnetic field impinging upon the cellular cultures. Its intensity remained well below 1.7 W/m2 during exposure.
- Citation: Calabrò E, Condello S, Currò M, Ferlazzo N, Caccamo D, Magazù S, Ientile R. Modulation of heat shock protein response in SH-SY5Y by mobile phone microwaves. World J Biol Chem 2012; 3(2): 34-40
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v3/i2/34.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v3.i2.34