Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Biol Chem. Jan 27, 2022; 13(1): 15-34
Published online Jan 27, 2022. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.15
Published online Jan 27, 2022. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.15
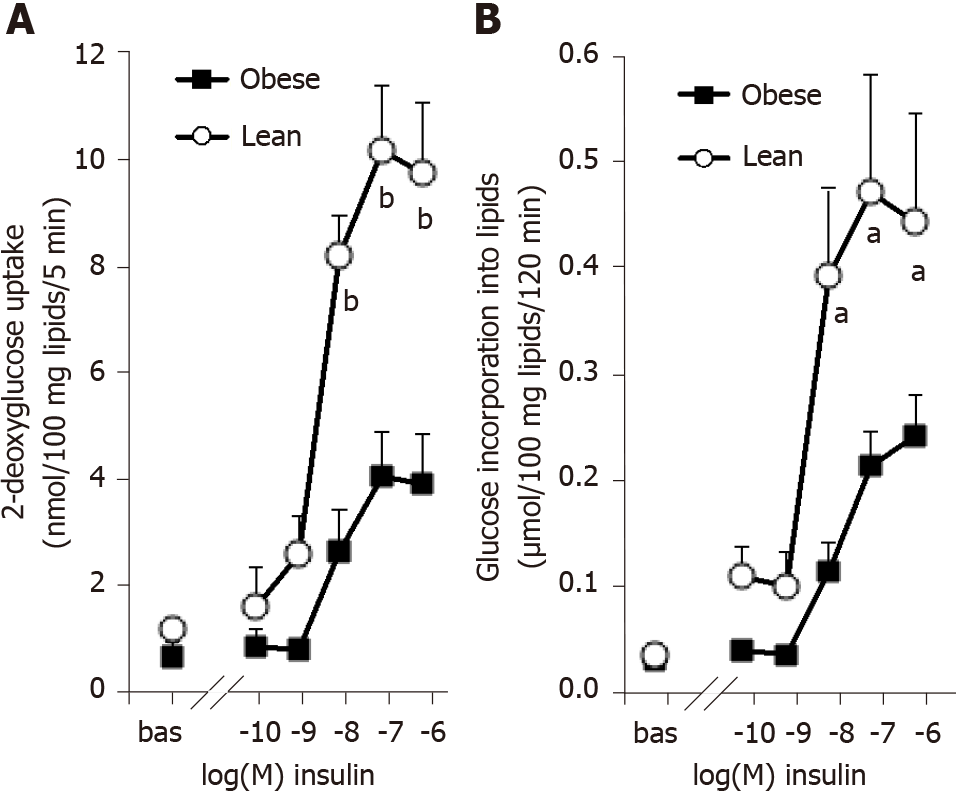
Figure 1 Influence of obesity on the dose-dependent responses of rat adipocytes to insulin activation of hexose uptake and of lipogenesis.
A: 3H-2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) transport was assayed for 5 min after 45-min incubation of rat fat cells without (bas) or with increasing doses of insulin. 2-DG uptake is expressed as nmoles of intracellular radiolabeled 2-DG/100 mg lipids/5 min; B: 3H-glucose incorporation into lipids was measured after 120-min incubation with the indicated doses of insulin and is expressed as µmoles tritiated glucose incorporated/100 mg lipids. Adipocytes from lean (open circles) or obese rats (black squares) were incubated at a cell suspension averaging 11.5 and 11.7 mg lipids/assay tube, respectively. A significant influence of genotype on the three higher doses of insulin was found at bP < 0.001 for 2-DG uptake (n = 10 lean and 10 obese male rats, with male/female = 1) and at aP < 0.05 for lipogenesis (n = 8 lean and 6 obese male rats). Each point is the mean ± SEM of n animals, with error bars lying within the caption in several occurrences.
- Citation: Carpéné C, Marti L, Morin N. Increased monoamine oxidase activity and imidazoline binding sites in insulin-resistant adipocytes from obese Zucker rats . World J Biol Chem 2022; 13(1): 15-34
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v13/i1/15.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.15