Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 27, 2021; 12(6): 104-113
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i6.104
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i6.104
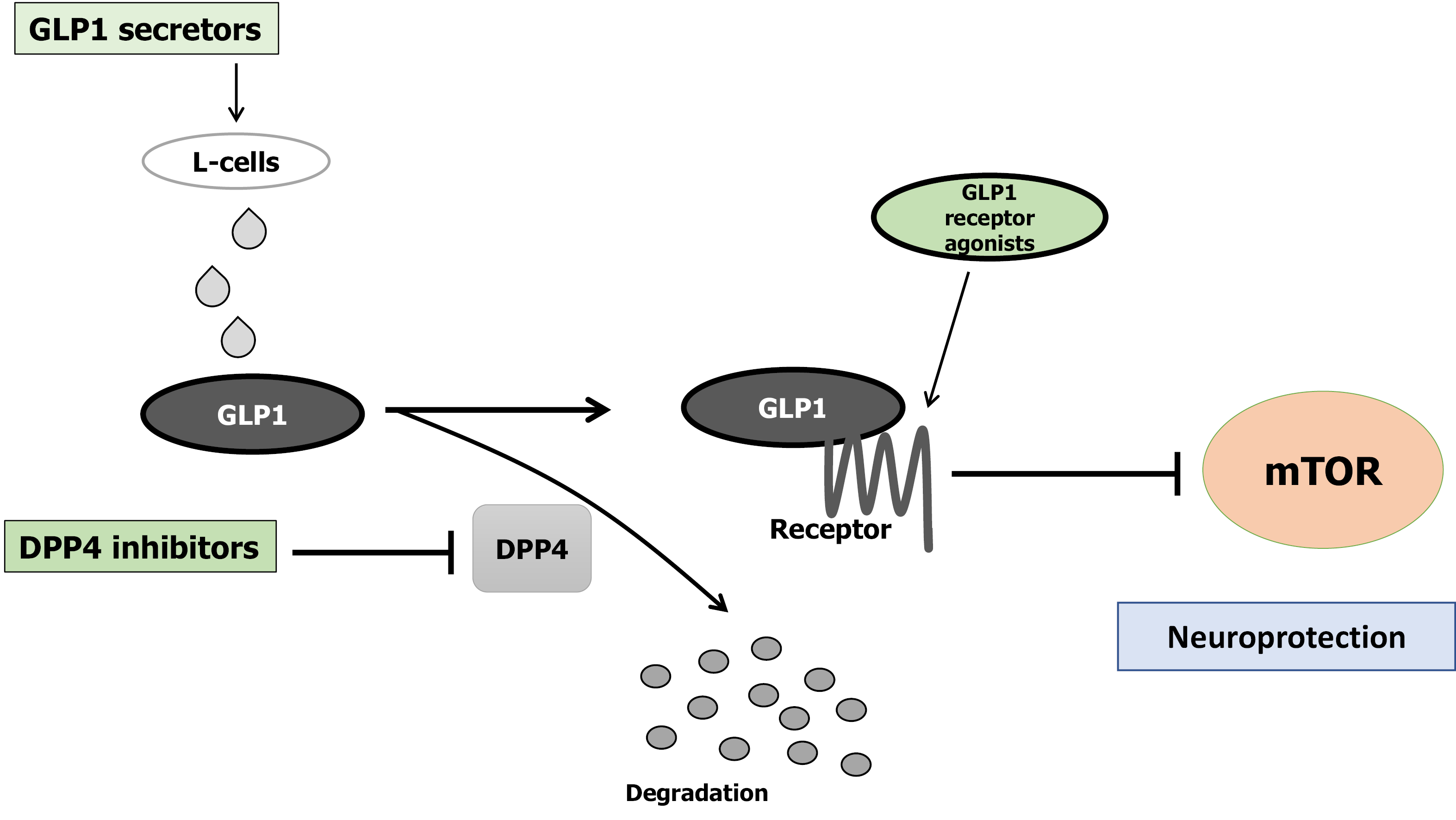
Figure 2 Implication of decreased dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 activity, increased Glucagon-like peptide-1, increased Glucagon-like peptide-1-receptor agonists, and decreased mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin activity for the neuroprotection.
Arrowhead means stimulation whereas hammerhead represents inhibition. Note that some critical pathways have been omitted for clarity. GLP1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; mTOR: Mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin; DPP4: Dipeptidyl-peptidase-4.
- Citation: Ikeda Y, Nagase N, Tsuji A, Kitagishi Y, Matsuda S. Neuroprotection by dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs via the modulation of AKT-signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. World J Biol Chem 2021; 12(6): 104-113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v12/i6/104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v12.i6.104