Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Biol Chem. Sep 27, 2021; 12(5): 87-103
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.87
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.87
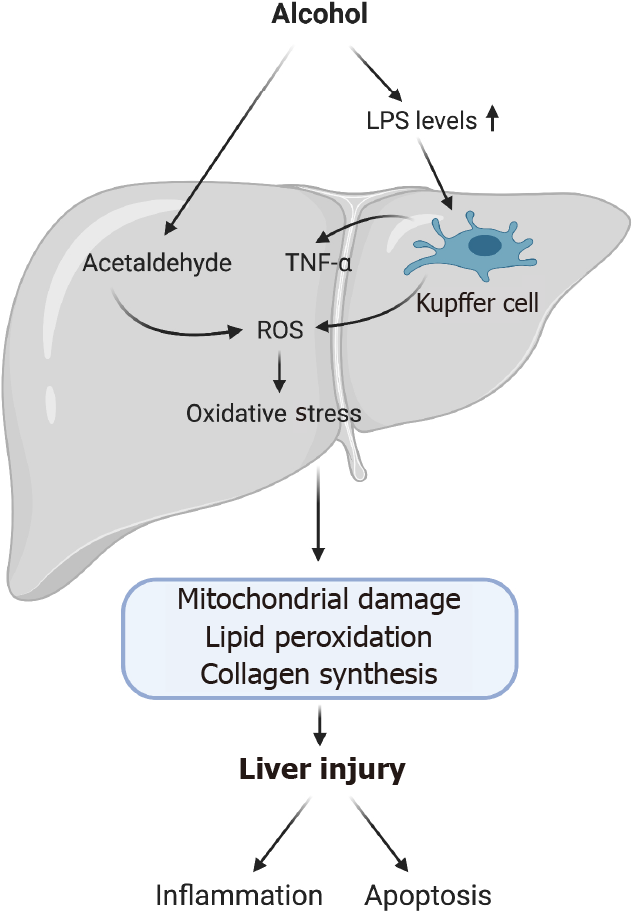
Figure 1 Alcohol-related induction of oxidative stress and liver injury.
Alcohol misuse leads to loss of tight junctions in the gut increasing its permeability. This causes translocation of lipopolysaccharide into the liver activating toll-like receptor 4 on Kupffer cells (KCs). Activation of KCs can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α. ROS production also occurs due to the metabolism of alcohol. ROS production and inflammatory cytokines leads to inflammation and recruitment of inflammatory cells as well as activation of apoptotic pathways. (Figure created with BioRender.com). LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Petagine L, Zariwala MG, Patel VB. Alcoholic liver disease: Current insights into cellular mechanisms. World J Biol Chem 2021; 12(5): 87-103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v12/i5/87.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.87