Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Biol Chem. Jan 27, 2021; 12(1): 1-14
Published online Jan 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i1.1
Published online Jan 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i1.1
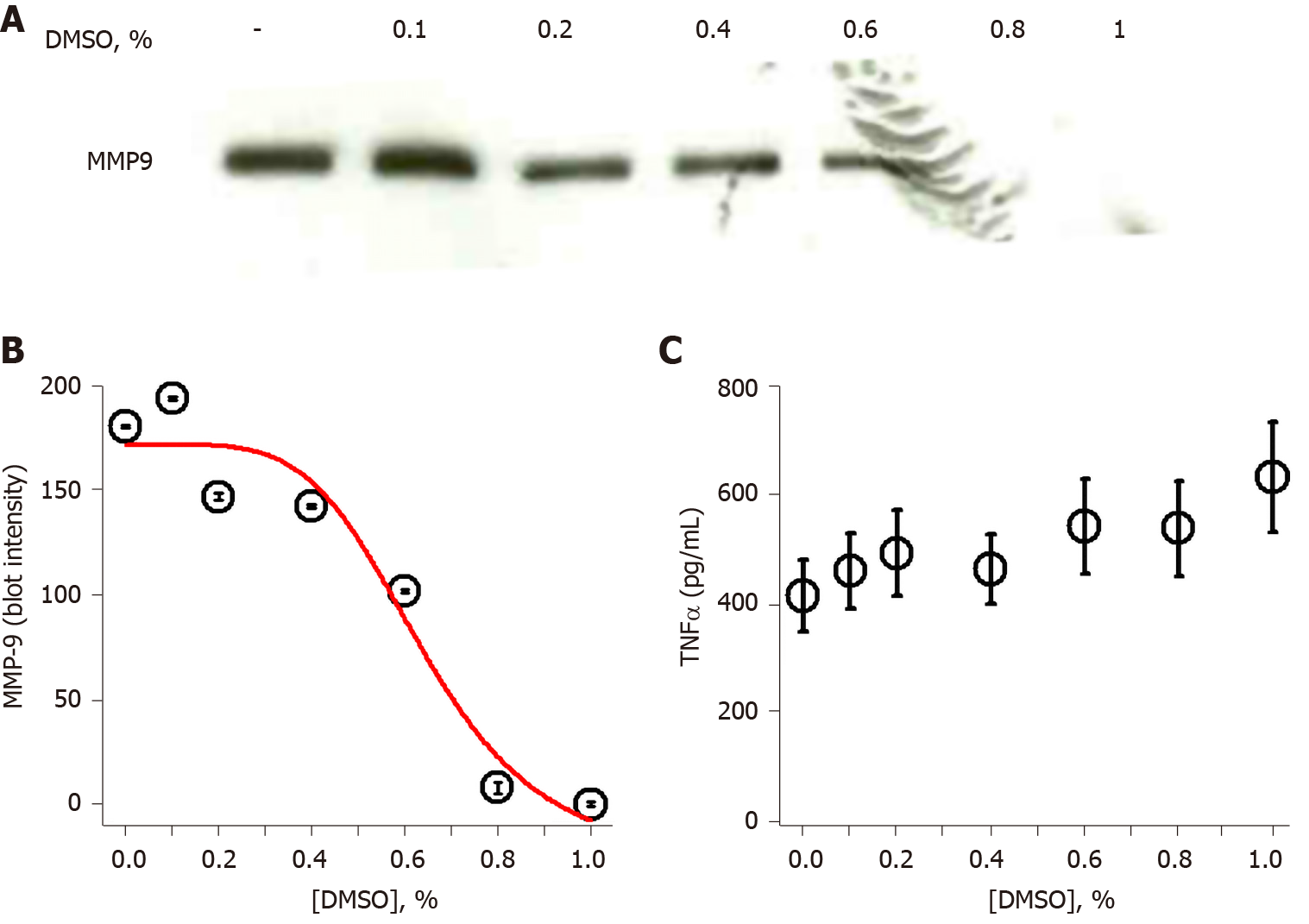
Figure 2 Dimethyl sulfoxide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced matrix-metalloproteinase-9 in a dose-dependent fashion.
A: SDS-PAGE/immunoblot of cell supernatants; B: Densitometry of Panel A. Each data bar is the average ± standard error for three independent densitometry measurements. Data were fit to a nonlinear inhibition equation, which produced an IC50 of 0.64%; and C: Tumor necrosis factor α levels were determined in cell supernatants by enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay and each data bar is the average ± standard error for three independent measurements. THP-1 monocytes were treated with a concentration range of dimethyl sulfoxide (0.1%-1%) followed by lipopolysaccharide (1 μg/mL) for 72 h. Cells were collected, centrifuged at 500 g for 10 min and supernatant assessed for (A) matrix-metalloproteinase-9 and (C) tumor necrosis factor α. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; MMP-9: Matrix-metalloproteinase-9; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α.
- Citation: Denner DR, Udan-Johns ML, Nichols MR. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion by dimethyl sulfoxide and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in human monocytes. World J Biol Chem 2021; 12(1): 1-14
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v12/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v12.i1.1