Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jul 26, 2010; 1(7): 209-220
Published online Jul 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i7.209
Published online Jul 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i7.209
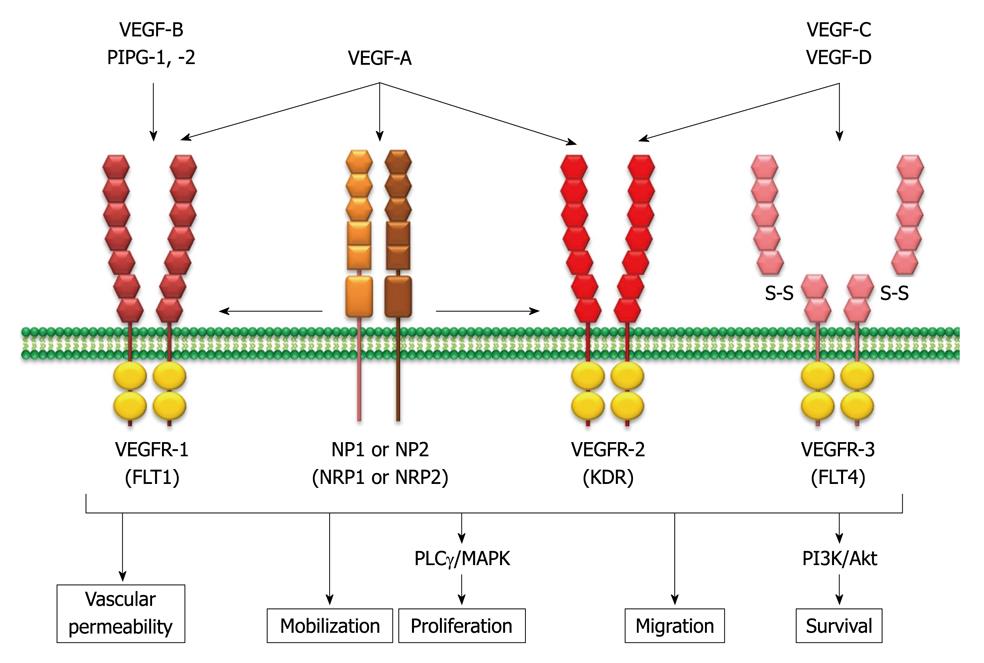
Figure 2 Vascular endothelium growth factor family members and their specific binding ligands.
The mammalian vascular endothelium growth factor (VEGF) family consists of seven structurally related glycoproteins with VEGF-A as the major mediator of tumor angiogenesis among them. The VEGF ligands bind to three structurally similar receptors, and each tyrosine kinase activates the intracellular signaling cascade, including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways. Subsequently, the pro-angiogenic signaling pathways are activated. PLCγ: Phospholipase C γ; NP: Neuropilin; VEGFR: VEGF receptors; FLT: Fms-related tyrosine kinase; KDR: Kinase insert domain receptor.
- Citation: Itamochi H. Targeted therapies in epithelial ovarian cancer: Molecular mechanisms of action. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(7): 209-220
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i7/209.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i7.209