Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jun 26, 2010; 1(6): 201-208
Published online Jun 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i6.201
Published online Jun 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i6.201
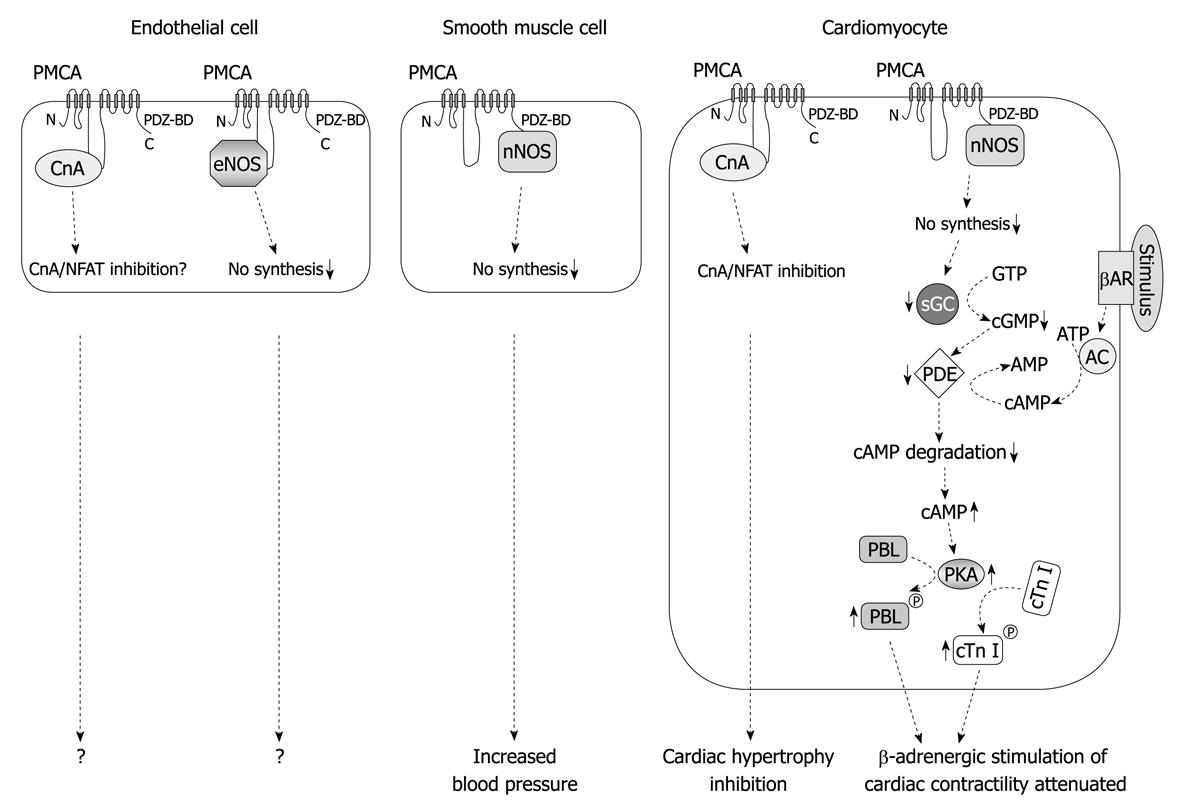
Figure 2 Physiological consequences of the interaction between PMCAs and signaling partner proteins in the cardiovascular system.
The figure depicts regulatory interactions between PMCA and calcium-dependent signaling proteins in cardiovascular cells. These interactions play a pivotal role in the regulation of cardiovascular physiology via regulation of the NO and calcineurin/NFAT signal transduction pathways. CnA: Calcineurin A; sGC: Soluble guanylyl cyclase; PDE: Phosphodiesterase; PKA: Protein kinase A; PBL: Phospholamban; cTn I: Cardiac troponin I; βAR: β-adrenergic receptor; AC: Adenylyl cyclase; NFAT: Nuclear factor of activated T cells.
- Citation: Holton ML, Wang W, Emerson M, Neyses L, Armesilla AL. Plasma membrane calcium ATPase proteins as novel regulators of signal transduction pathways. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(6): 201-208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i6/201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i6.201