Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2010; 1(5): 188-195
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.188
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.188
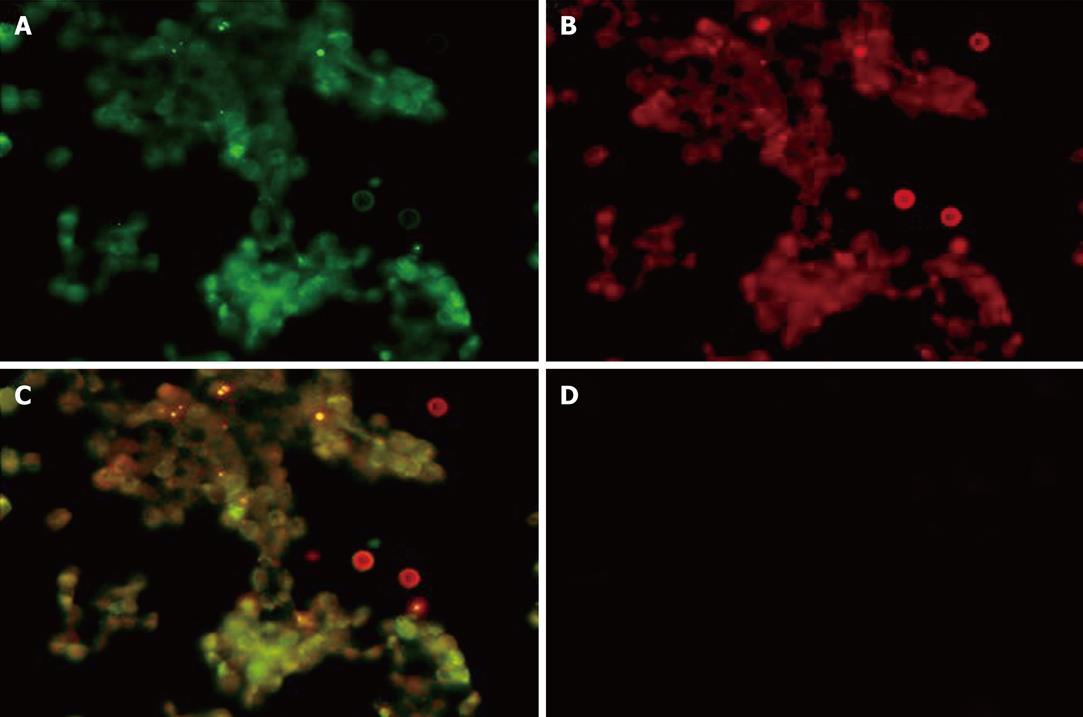
Figure 5 Intracellular localization of fluorescent-labeled ricin and MTS-conjugated dgA Ab by immunofluorescent staining.
A: Immunofluorescent staining of RAW264.7 cells treated with Alexa 488-labeled ricin (green); B: MTS-conjugated dgA Ab detected by TRITC-labeled anti-mouse IgG (red); C: Superposition of A and B demonstrated co-localization of ricin and MTS-dgA Ab (yellow); D: Immunofluorescent staining of RAW264.7 cells treated with unconjugated dgA Ab and detected with TRITC-labeled anti-mouse IgG. No staining was observed, demonstrating the inability of unconjugated dgA Ab to enter cells.
- Citation: Wu F, Fan S, Martiniuk F, Pincus S, Müller S, Kohler H, Tchou-Wong KM. Protective effects of anti-ricin A-chain antibodies delivered intracellularly against ricin-induced cytotoxicity. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(5): 188-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i5/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.188