Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2010; 1(5): 109-132
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.109
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.109
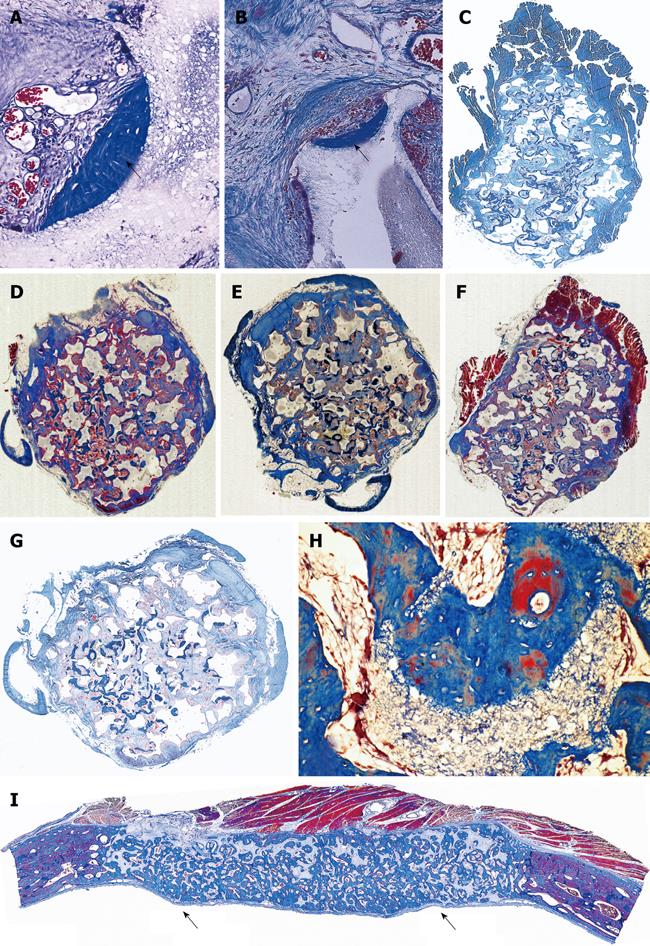
Figure 12 Bone induction regulated by a series of repetitive concavities assembled within the macroporous spaces of highly crystalline sintered hydroxyapatite implanted in the rectus abdominis of non-human primates P.
ursinus. A, B: Bone (short arrows) with associated vascular invasion initiates within concavities of heterotopically implanted substrata. Devices were implanted in the rectus abdominis muscle without the addition of osteogenic proteins of the TGF-β supergene family; C-G: Macroporous sintered calcium phosphate constructs harvested from the rectus abdominis on day 90: low power views of five specimens harvested from different animals showing the reproducible intrinsic induction of bone formation by the geometric motif of the concavity highlighted in (H); I: Low power view of the prominent induction of bone formation (short arrows) across the macroporous spaces of a sintered construct on day 90 previously implanted in a calvarial defect. Decalcified sections cut at 6 μm and stained with Goldner’s trichrome.
- Citation: Ripamonti U. Soluble and insoluble signals sculpt osteogenesis in angiogenesis. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(5): 109-132
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i5/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.109