Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2010; 1(5): 109-132
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.109
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.109
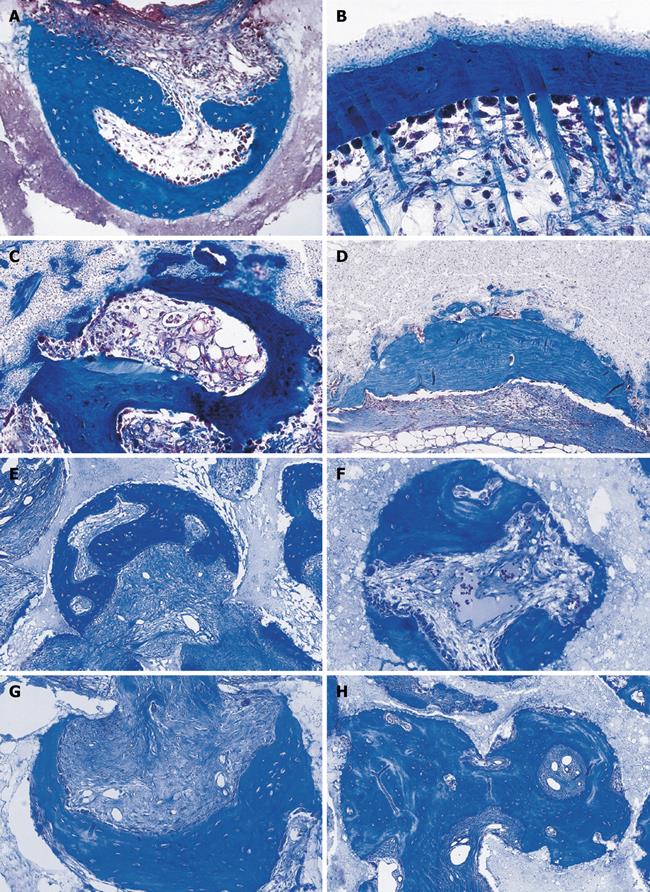
Figure 11 Self inducing geometric cues: the concavity and the induction of bone differentiation by carbon-impregnated single-phase hydroxyapatite biomatrices and biphasic hydroxyapatite/tricalcium phosphate biomimetic matrices.
A, B: Prominent osteogenesis within carved concavities of carbon-impregnated single phase hydroxyapatite biomatrices 90 d after heterotopic implantation; B: Induction of bone formation by fine carbon-impregnated single phase hydroxyapatite with collagenic compact fibers protruding between osteoblastic cells into the fibrovascular space of the concavity; C: Induction of bone formation along a concavity of coarse carbon-impregnated hydroxyapatite scaffold inducing bone also in the bulk of the sintered construct; D: Maintenance and remodeling of the newly formed bone 180 d after heterotopic implantation of carbon-impregnated single-phase hydroxyapatite coarse biomatrix; E-H: Induction of bone in macroporous spaces with concavities initiating and maintaining the induction of bone formation 90 and 180 d after intramuscular implantation. Decalcified sections cut at 6 μm and stained with Goldner’s trichrome.
- Citation: Ripamonti U. Soluble and insoluble signals sculpt osteogenesis in angiogenesis. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(5): 109-132
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i5/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.109