Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Dec 26, 2010; 1(12): 353-361
Published online Dec 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i12.353
Published online Dec 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i12.353
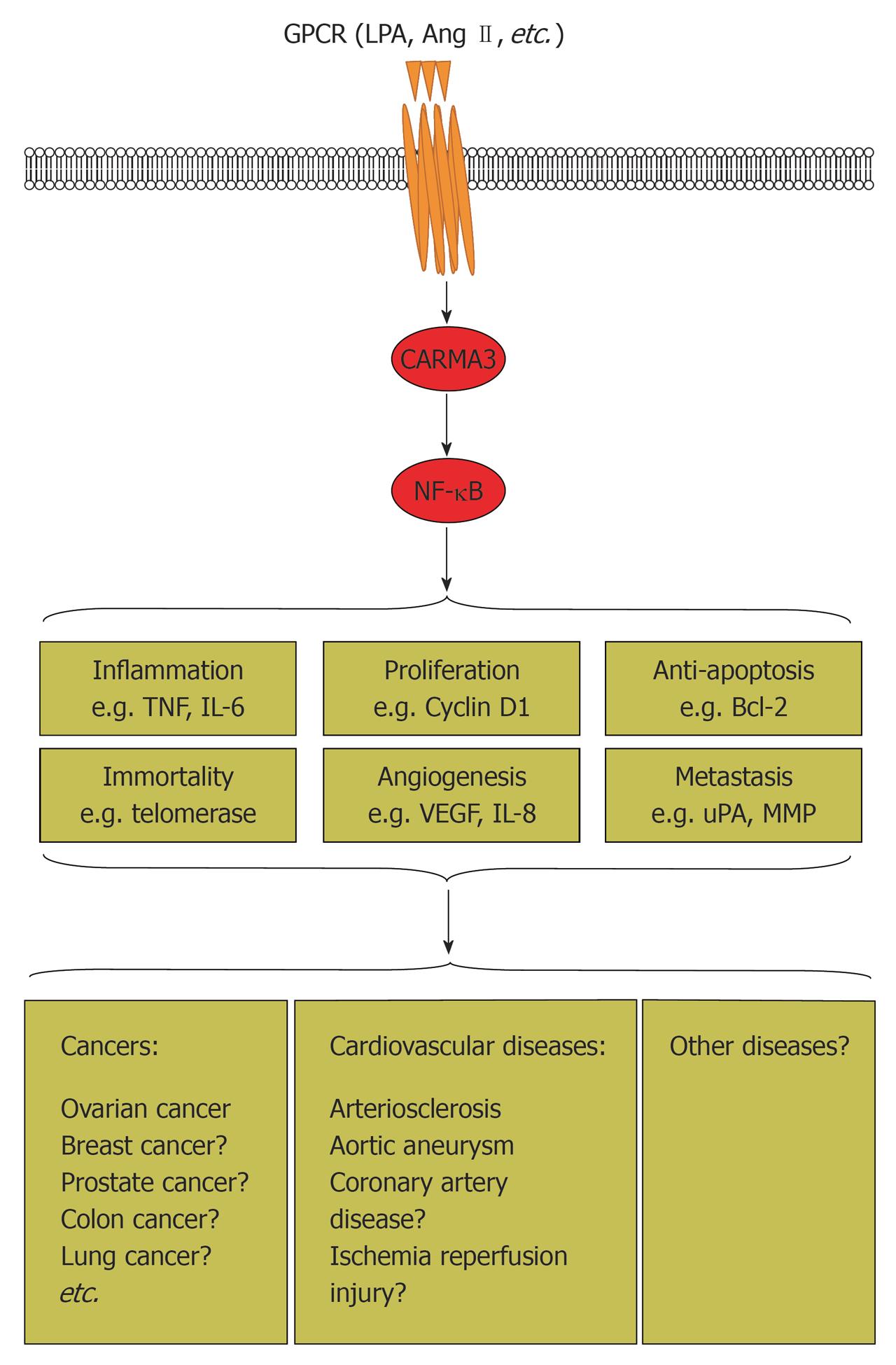
Figure 3 Proposed working model of G protein-coupled receptor/CARD recruited membrane associated protein 3/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways in cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and other diseases.
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) [lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), angiotensin (Ang) II] activates CARD recruited membrane associated protein 3 (CARMA3), which in turn triggers nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation. NF-κB plays an important role in regulation of many physiological and pathological processes. Aberrant regulation of the GPCR/CARMA3/NF-κB signaling axis results in cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and probably other diseases. Mechanistically, it promotes cell proliferation, angiogenesis and metastasis, and inhibits apoptosis. In addition, it also induces inflammation. CARMA3 is indispensable for GPCR (LPA, Ang II)-induced NF-κB activation. Consequently, it plays pivotal roles in GPCR-induced tumor progression and cardiovascular diseases. Full definition of GPCR/CARMA3/NF-κB signaling events could aid the discovery of new drug targets and production of profoundly significant clinical therapies for cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and many other diseases. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; uPA: Urokinase plasminogen activator; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases.
- Citation: Sun J. CARMA3: A novel scaffold protein in regulation of NF-κB activation and diseases. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(12): 353-361
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i12/353.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i12.353