Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Oct 26, 2010; 1(10): 298-306
Published online Oct 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.298
Published online Oct 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.298
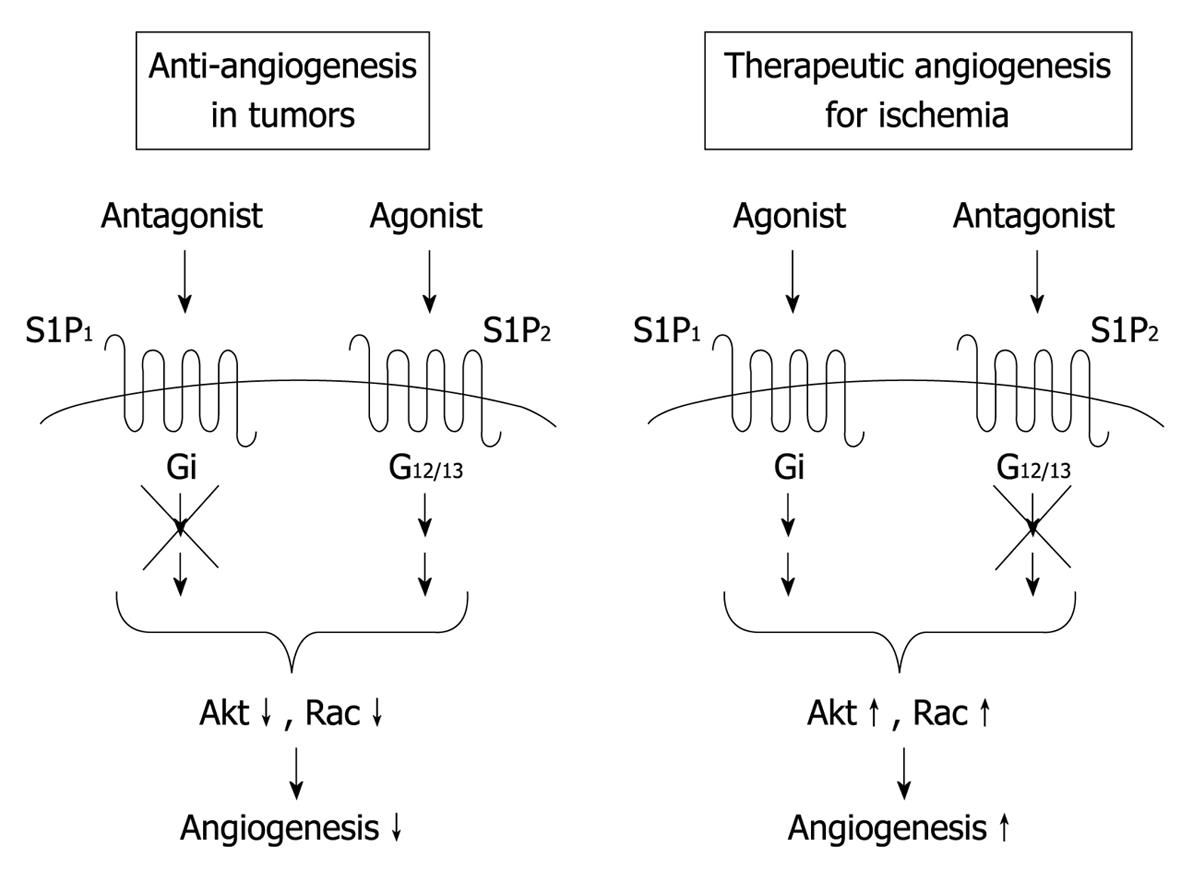
Figure 3 Possible therapeutic strategies for anti-angiogenesis in tumors and angiogenesis in ischemic diseases.
S1P1 and S1P2 mediate angiogenic and anti-angiogenic effects of S1P in vivo, respectively. Therefore, it is possible that simultaneous activation of the angiogenic receptor S1P1 and blockade of the anti-angiogenic receptor S1P2 are more effective for therapeutic angiogenesis in ischemic diseases compared with S1P1 activation or S1P2 inhibition alone. In contrast, for anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer, the combination of S1P1 inhibition and S1P2 stimulation might be favorable.
- Citation: Takuwa Y, Du W, Qi X, Okamoto Y, Takuwa N, Yoshioka K. Roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in angiogenesis. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(10): 298-306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i10/298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.298