Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2014; 6(11): 229-234
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i11.229
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i11.229
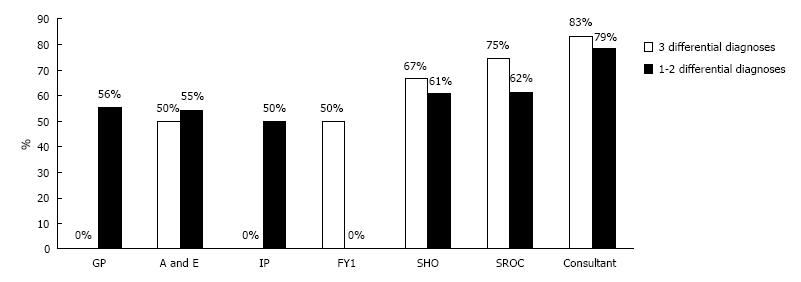
Figure 3 Percentage of correct diagnoses made with 3 differential diagnoses vs 1-2 differential diagnoses.
The use of 3 differential diagnoses among the surgical team (FY1, SHO, SROC, and Consultant) improved diagnostic accuracy by 8.1% (73.3% vs 65.2%). Referring physicians did not follow this trend. GP: General practitioner; IP: In-patient referrer; FY1: Foundation year-1; SHO: Senior house officer; SROC: Surgical registrar on-call.
- Citation: Sajid MS, Hollingsworth T, McGlue M, Miles WF. Factors influencing the diagnostic accuracy and management in acute surgical patients. World J Gastrointest Surg 2014; 6(11): 229-234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v6/i11/229.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v6.i11.229