Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2025; 17(1): 97148
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.97148
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.97148
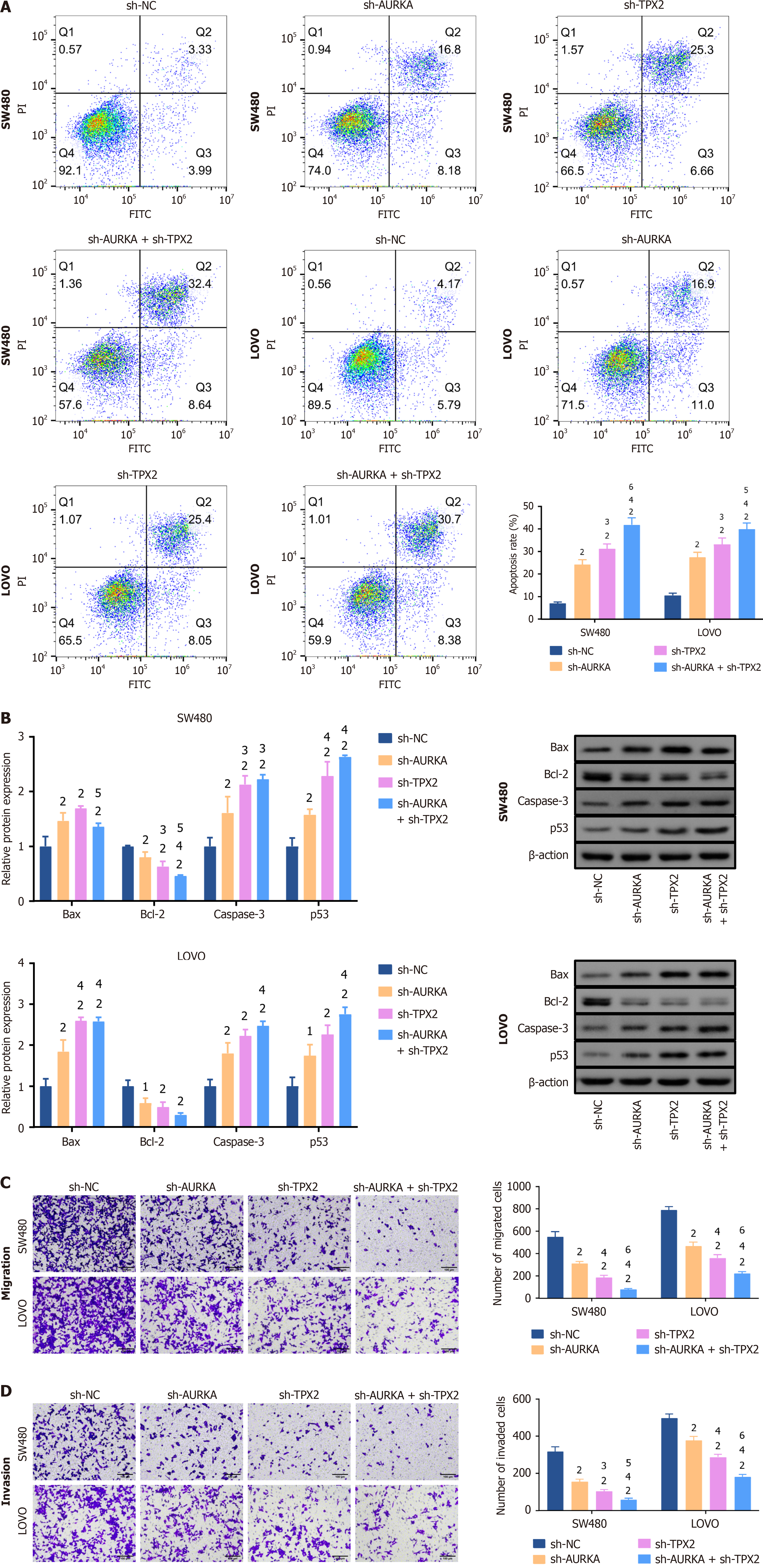
Figure 6 Knockdowns of Aurora A and targeting protein for Xklp2 promoted colorectal cancer cell apoptosis and inhibited cell migration and invasion.
A: Cell apoptosis in SW480 and LOVO cells was determined by flow cytometry. Apoptosis cells were increased in Aurora kinase A (AURKA)/targeting protein for Xklp2 (TPX2) knockdown or co-knockdown cells; B: Western blotting was used to detect the expression levels of apoptosis-related biomarkers. B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)-associated X protein, caspase 3, and tumor protein P53 expression levels were increased in SW480 and LOVO cells with AURKA/TPX2 knockdown or co-knockdown, while Bcl-2 was decreased; C: The number of migrated cells; D: Invaded cells was decreased in SW480 and LOVO cells with AURKA/TPX2 knockdown or co-knockdown. Transwell assay was used to detect cell migration and invasion abilities. 1P < 0.05 vs negative control of short hairpin RNA (sh-NC) group. 2P < 0.01 vs sh-NC group. 3P < 0.05 vs short hairpin RNA of AURKA (sh-AURKA) group. 4P < 0.01 vs sh-AURKA group. 5P < 0.05 vs short hairpin-TPX2 (sh-TPX2) group. 6P < 0.01 vs sh-TPX2 group. AURKA: Aurora kinase A; TPX2: Targeting protein for Xklp2; sh-NC: Negative control of short hairpin RNA; sh-AURKA: Short hairpin RNA of Aurora kinase A; sh-TPX2: Short hairpin RNA of targeting protein for Xklp2; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: B-cell lymphoma-2 associated X protein; p53: Tumor protein P53; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI: Propidium iodide.
- Citation: Sheng GX, Zhang YJ, Shang T. Synergistic inhibition of colorectal cancer progression by silencing Aurora A and the targeting protein for Xklp2. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(1): 97148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i1/97148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.97148