Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2024; 16(6): 1592-1600
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1592
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1592
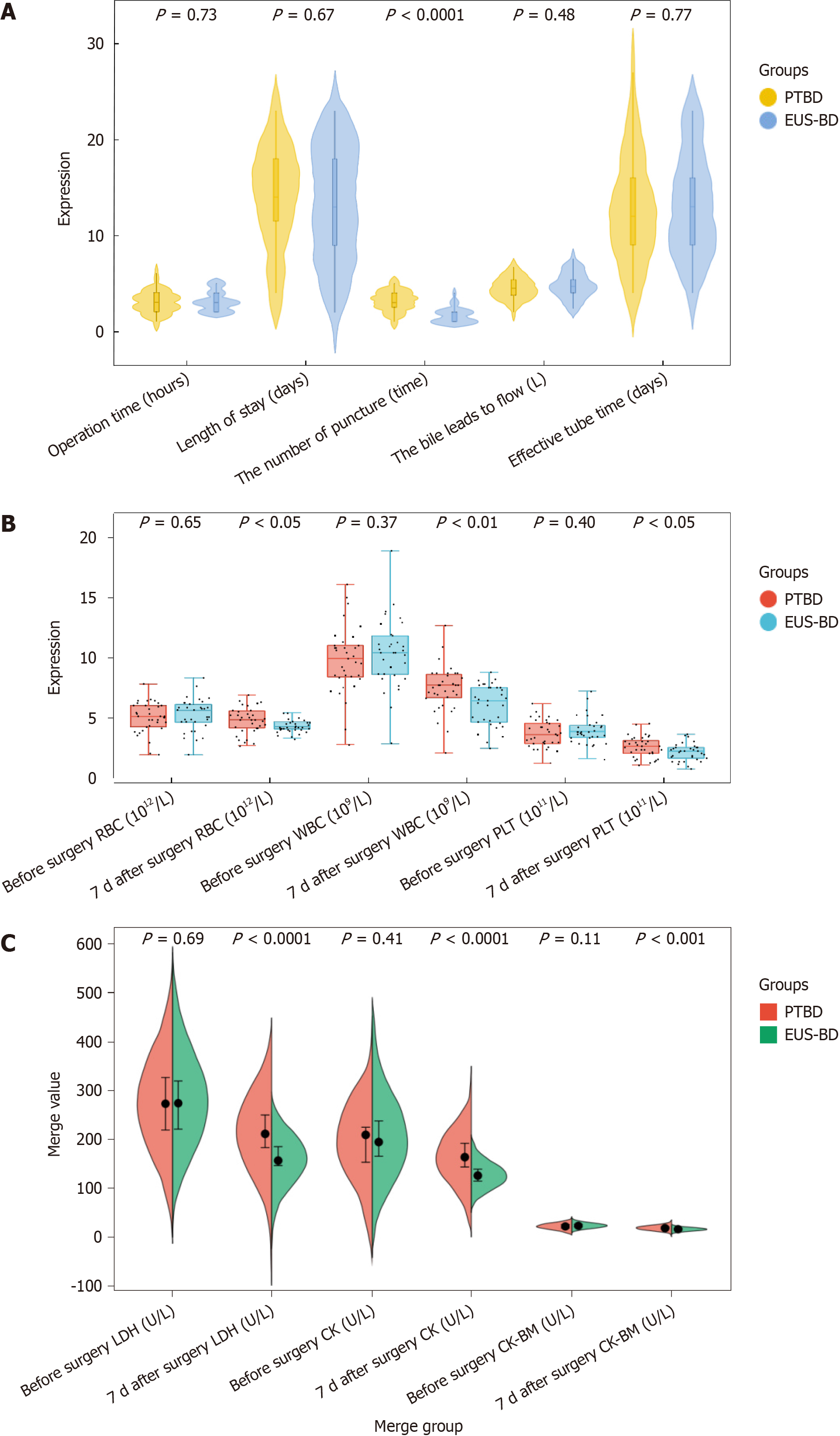
Figure 1 Comparison of procedure-related measures, routine blood parameters, and myocardial function measures between the endo
- Citation: Zhu QQ, Chen BF, Yang Y, Zuo XY, Liu WH, Wang TT, Zhang Y. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage vs percutaneous transhepatic bile duct drainage in the management of malignant obstructive jaundice. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(6): 1592-1600
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i6/1592.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1592