Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Sep 27, 2022; 14(9): 976-985
Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.976
Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.976
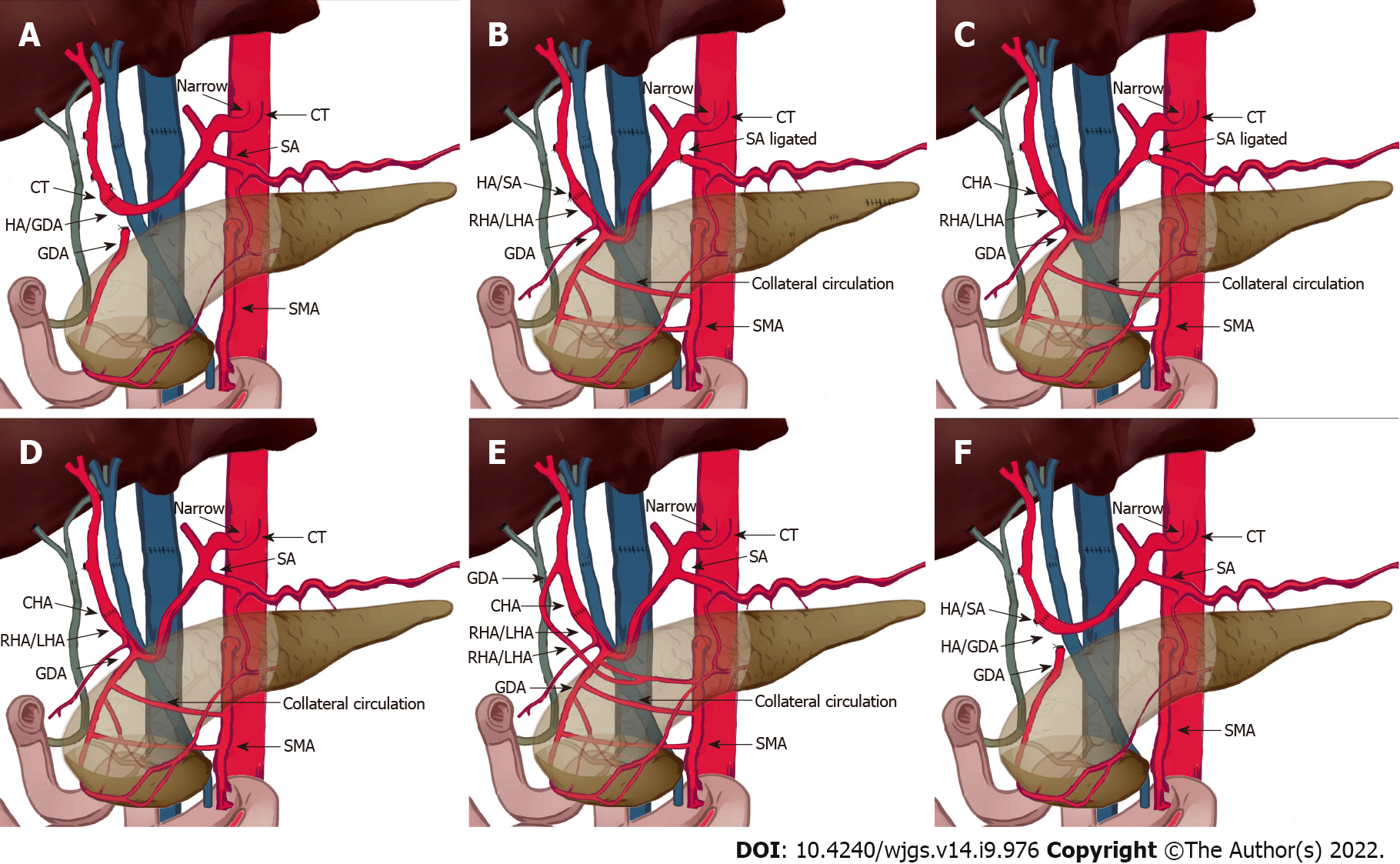
Figure 3 Schematic diagram showing different types of patch anastomoses performed in this study.
A: Donor: celiac trunk; recipient: hepatic/gastroduodenal artery (GDA) patch. Median arcuate ligament (MAL) was divided. Splenic artery was not ligated; B: Donor: hepatic/splenic artery (HA/SA) patch; recipient: right/left hepatic artery (RHA/LHA) patch; MAL was not divided. GDA was preserved. Splenic artery was ligated; C: Donor: common hepatic artery (CHA); recipient: RHA/LHA patch; MAL was not divided. GDA was preserved. Splenic artery was ligated; D: Donor: CHA; recipient: RHA/LHA patch; MAL was not divided. GDA was preserved. Splenic artery was not ligated; E: Donor: (1) GDA; and (2) CHA; recipient: (1) aberrant right hepatic artery; and (2) right/left hepatic artery patch; MAL was not divided. GDA was preserved. Splenic artery was not ligated; F: Donor: HA/SA patch; recipient: hepatic/GDA patch; MAL was not divided. Splenic artery was not ligated. MAL: Median arcuate ligament; CT: Computed tomography; HA/SA: Hepatic artery/splenic artery; RHA/LHA: Right/left hepatic artery; GDA: Gastroduodenal artery; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; CHA: Common hepatic artery.
- Citation: Li SX, Fan YH, Tian GY, Lv GY. Feasible management of median arcuate ligament syndrome in orthotopic liver transplantation recipients. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(9): 976-985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i9/976.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.976