Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1448-1462
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1448
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1448
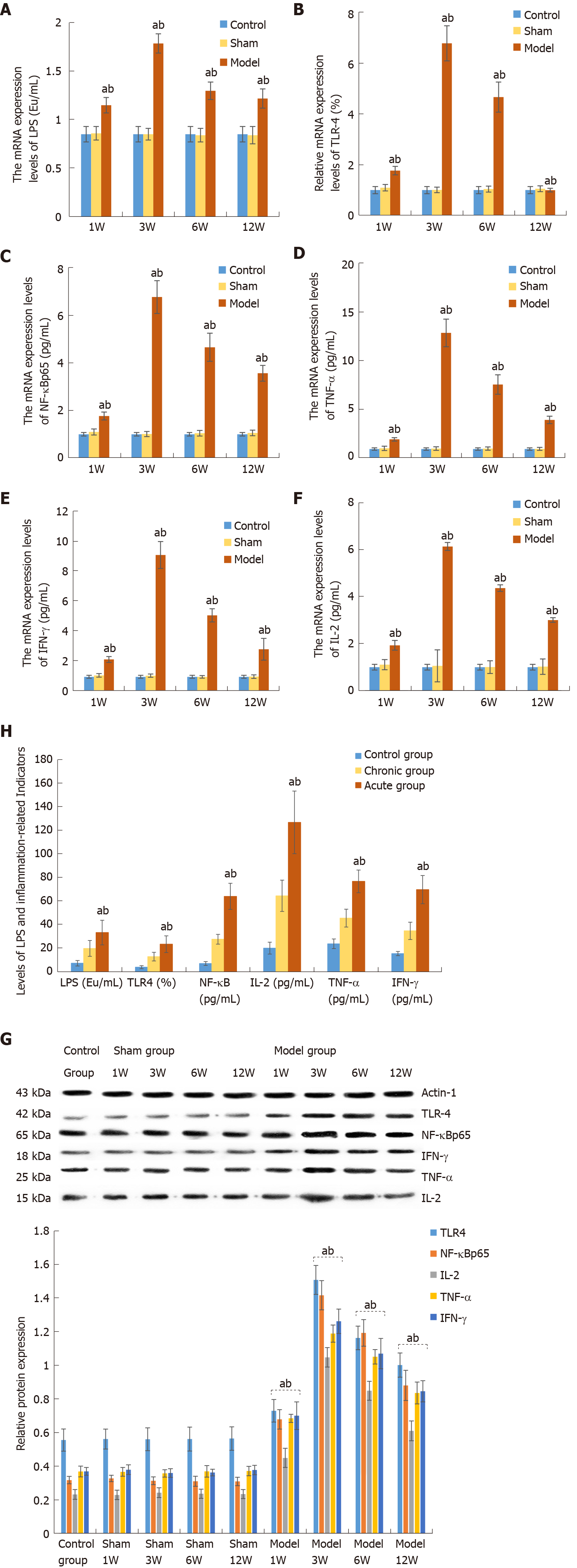
Figure 2 Hepatic mRNA and protein expression levels of lipopolysaccharide and various factors in rats and humans.
A: The expression levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in each group; B: TLR4 expression in each group; C: Nuclear factor-kappa B p65 expression in each group; D: Tumor necrosis factor-α expression in each group; E: Interferon-γ expression in each group; F: Interleukin-2 expression in each group; G: Western blot analysis of protein express levels of various factors in the rat liver tissues; H: Levels of LPS and TLR4/NF-κB mediated inflammation-related indicators in the blood samples from human subjects. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-2: Interleukin-2; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ. aP < 0.05 comparisons between subgroups. bP < 0.05 comparisons between model subgroups.
- Citation: Li J, Chen XM, Zhou CZ, Fang WW, Lv WF, Cheng DL. Novel roles of lipopolysaccharide and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in inflammatory response to liver injury in Budd-Chiari syndrome. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(11): 1448-1462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i11/1448.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1448