Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1315-1326
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1315
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1315
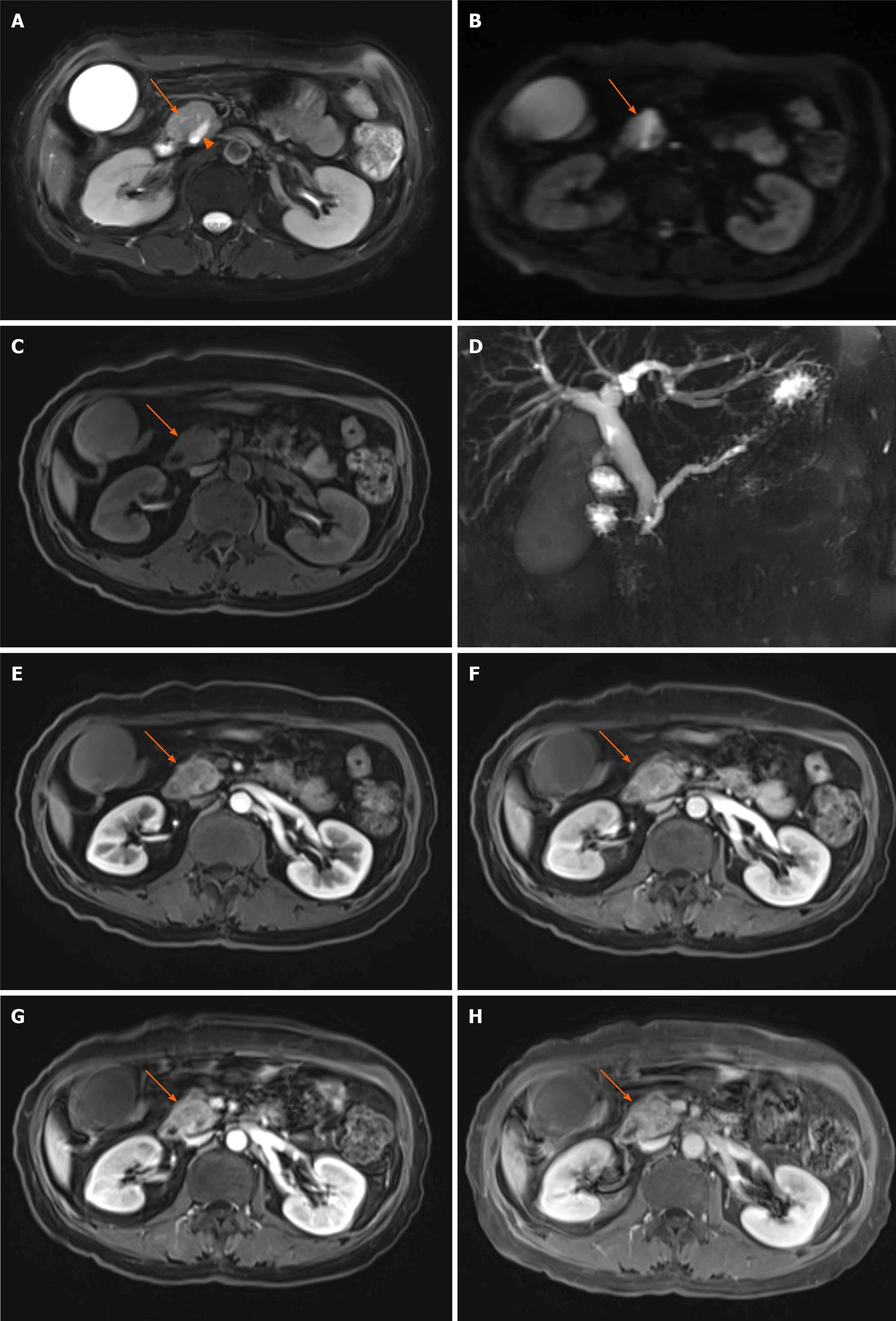
Figure 4 Typical magnetic resonance features of pancreatic head carcinoma in a 57-year-old female patient.
A–C: Swollen pancreatic head (arrow) with slightly higher signal on T2-weighted imaging (WI) (A) and diffusion-weighted imaging (B), and low signal on T1WI (C) was detected; D: Notes that the dilation of pancreatic duct (arow head) and double duct sign on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; E–H: After administration of contrast agent, the tumor shows a progressive enhancement pattern similar to computed tomography on early arterial phase (E), late arterial phase (F), venous phase (G), and delay phase (H).
- Citation: Feng P, Cheng B, Wang ZD, Liu JG, Fan W, Liu H, Qi CY, Pan JJ. Application and progress of medical imaging in total mesopancreas excision for pancreatic head carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(11): 1315-1326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i11/1315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1315