Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2018; 10(9): 95-106
Published online Dec 27, 2018. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v10.i9.95
Published online Dec 27, 2018. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v10.i9.95
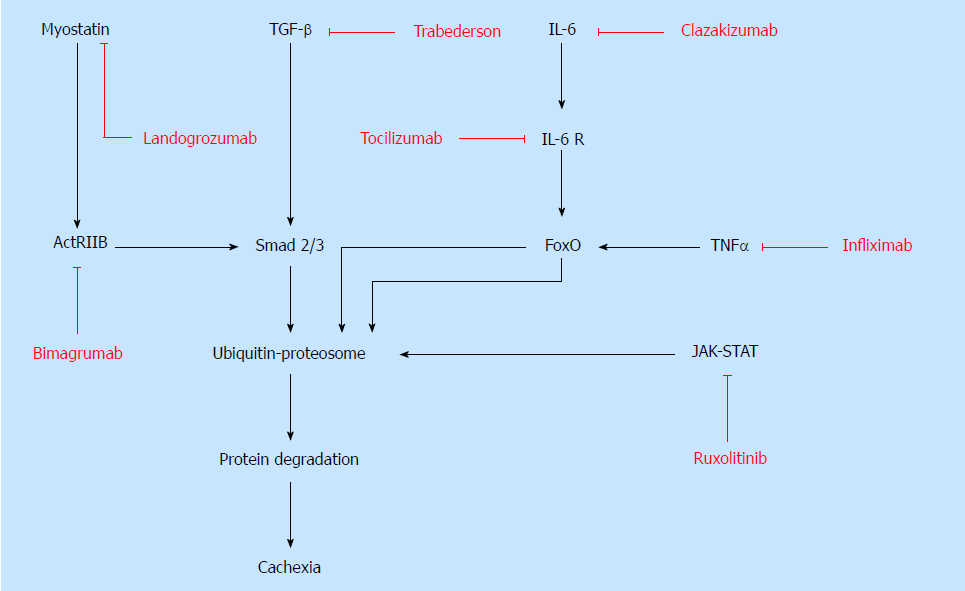
Figure 1 Signaling pathways involved in the pathophysiology of cachexia and targeted therapies.
Multiple molecular signaling pathways and mediators lead to protein degradation and cancer cachexia including myostatin/ActRIIB, TGF-β, Smad 2/3, IL-6, TNFα, FoxO and JAK-STAT. These molecular signaling pathways serve as therapeutic strategies for treatment of cachexia. Pharmacologic inhibitors that have been used clinically or experimentally are labelled in red and specific targets are notated. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; ActRIIB: Activin type IIB.
- Citation: Yakovenko A, Cameron M, Trevino JG. Molecular therapeutic strategies targeting pancreatic cancer induced cachexia. World J Gastrointest Surg 2018; 10(9): 95-106
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v10/i9/95.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v10.i9.95