Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2017; 8(5): 187-201
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.187
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.187
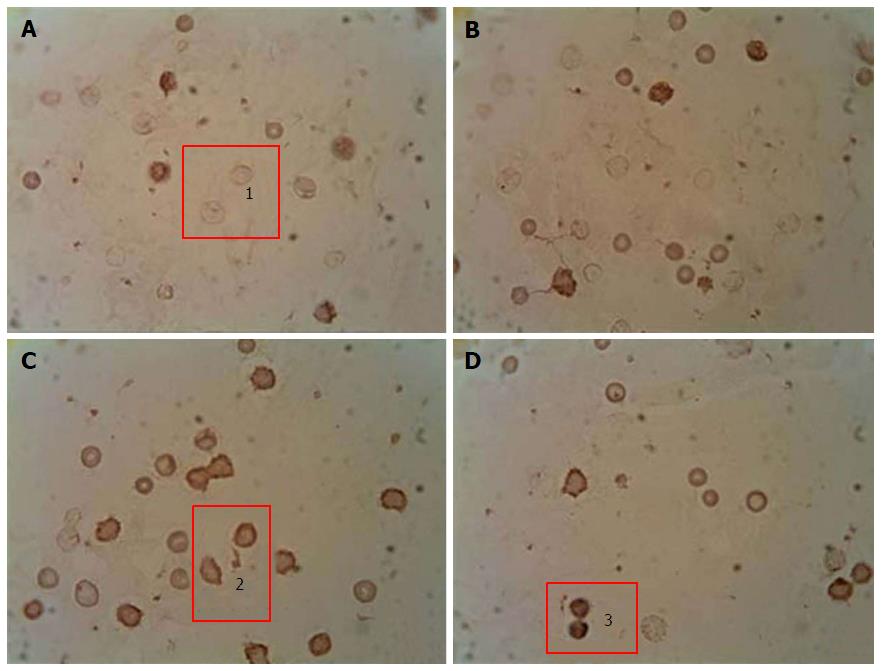
Figure 2 Immunocytochemical analysis of peripheral blood leukocytes in rats depending on the content of p53 pro-apoptotic protein in healthy animals, animals with streptozotocin-induced diabetes and treated with submerged cultured mycelium powder of mushrooms.
A: Control; B: Control animals treated with Agaricus brasiliensis (A. brasiliensis); С: Animals with STZ-induced diabetes mellitus; D: Diabetic animals treated with A. brasiliensis. 1: p53-; 2: p53+; 3: p53++. An indirect immunoperoxidase method was used for detection and visualization of intracellular protein p53. The content analysis of p53 in leukocytes of rat peripheral blood was performed by light microscopy using a × 40 microscope objective. Depending on intensity of staining, the cells were divided into 3 groups: Negative reaction (p53-), positive reaction (p53+), and high-positive (p53++) reaction.
- Citation: Vitak T, Yurkiv B, Wasser S, Nevo E, Sybirna N. Effect of medicinal mushrooms on blood cells under conditions of diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(5): 187-201
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i5/187.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.187