Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2017; 8(4): 143-153
Published online Apr 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.143
Published online Apr 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.143
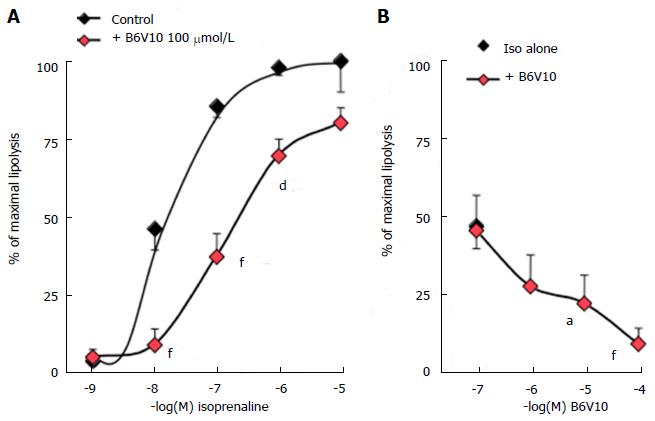
Figure 1 Influence of B6V10 on isoprenaline-induced lipolysis in rat adipocytes.
Glycerol release was determined in rat fat cells incubated 90 min without (basal) and with increasing concentrations of isoprenaline alone (control, black symbols) or with the indicated doses of B6V10. Basal lipolysis (0.39 ± 0.06 μmol glycerol/100 mg lipid/90 min) was set at 0% while maximal lipolytic effect of 10 μmol/L isoprenaline (1.73 ± 0.14 μmol glycerol/100 mg lipid/90 min) was set at 100%. A: Antilipolytic effect of 100 μmol/L B6V10 (red diamonds) on dose-dependent activation by isoprenaline; B: Dose-dependent inhibition by B6V10 of the lipolysis induced by 10 nmol/L isoprenaline (iso alone). Mean ± SEM of 8-10 determinations. Significantly different from corresponding condition without B6V10 at: aP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001.
- Citation: Carpéné C, Garcia-Vicente S, Serrano M, Marti L, Belles C, Royo M, Galitzky J, Zorzano A, Testar X. Insulin-mimetic compound hexaquis (benzylammonium) decavanadate is antilipolytic in human fat cells. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(4): 143-153
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i4/143.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.143