Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2017; 8(2): 56-65
Published online Feb 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i2.56
Published online Feb 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i2.56
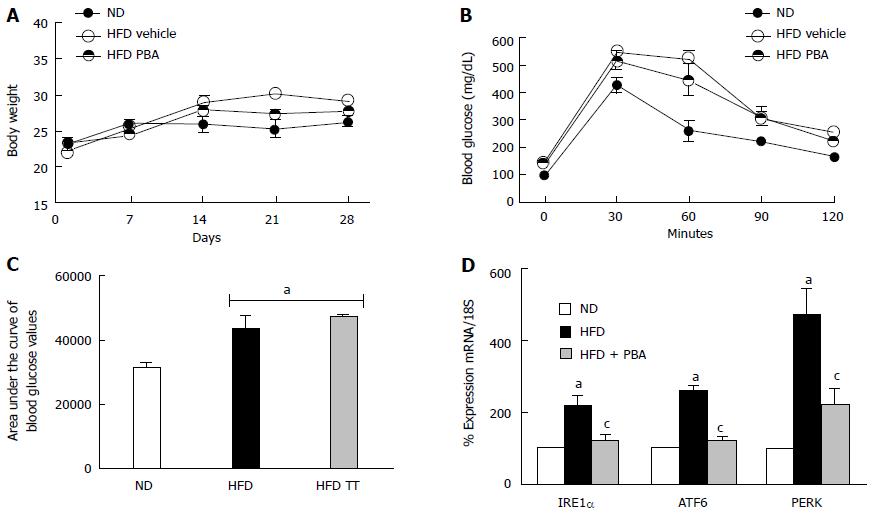
Figure 3 PBA mitigated high fat diet-mediated endoplasmic-reticulum-stress.
A: Total body weight (g) recorded weekly for 4 wk was not changed among the different groups; B: Glucose tolerance was impaired after 4 wk of HFD compared to ND, and was not restored with PBA treatment; C: Statistical analysis of area under the curve showing an increase in blood glucose levels in HFD compared to ND, which was not reversed by the treatment; D: Realtime PCR showing significant increases in IRE1α, ATF6, and PERK mRNA levels in mice kept on HFD for 4 wk compared to ND, which were nullified with PBA treatment (aP < 0.05 vs ND, cP < 0.05 vs HFD, n = 3-4). ND: Normal diet; HFD: High fat diet; PBA: Phenyl-butyric acid; PERK: Protein Kinase RNA-like endoplasmic-reticulum kinase; IRE: Inositol requiring enzyme.
- Citation: Coucha M, Mohamed IN, Elshaer SL, Mbata O, Bartasis ML, El-Remessy AB. High fat diet dysregulates microRNA-17-5p and triggers retinal inflammation: Role of endoplasmic-reticulum-stress. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(2): 56-65
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i2/56.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i2.56