Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. May 10, 2016; 7(9): 189-197
Published online May 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i9.189
Published online May 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i9.189
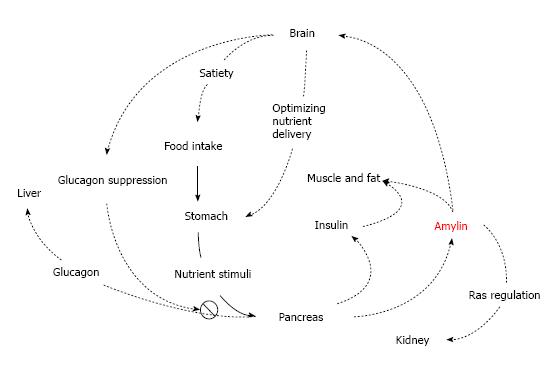
Figure 1 Overview of physiological actions of amylin.
(1) Amylin suppresses glucagon secretion from islet alpha cells at mealtime and thus, inhibits glucagons-induced glucose release from the liver; (2) Amylin delays nutrient delivery from the stomach to the small intestine for absorption; (3) Amylin reduces food intake by a signal mediated through the central nervous system; (4) Renal amylin may stimulate Renin-Angiotensin System; and (5) Amylin and insulin coordinate storage of carbohydrate.
- Citation: Zhang XX, Pan YH, Huang YM, Zhao HL. Neuroendocrine hormone amylin in diabetes. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(9): 189-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i9/189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i9.189